

 Investigate Alabama's Forests
Investigate Alabama's Forests
 |
A forest is simply an area of land mostly covered in trees. Forests cover approximately 1/3 of the planet and are home to most of its plants and terrestrial animals (those that live on land).
Forests cover about 70% of Alabama's land and play a very important role in our state's biodiversity (its variety of plants and animals), economy (the way people spend or make money), air and water quality, and culture.
| Click on the categories below to learn more about Alabama's forests. |
||
| Forest Types | Forests In Alabama | Importance of Forests |
| Forest Types | |
There are three main types of forests. Each type is defined by:
|
|
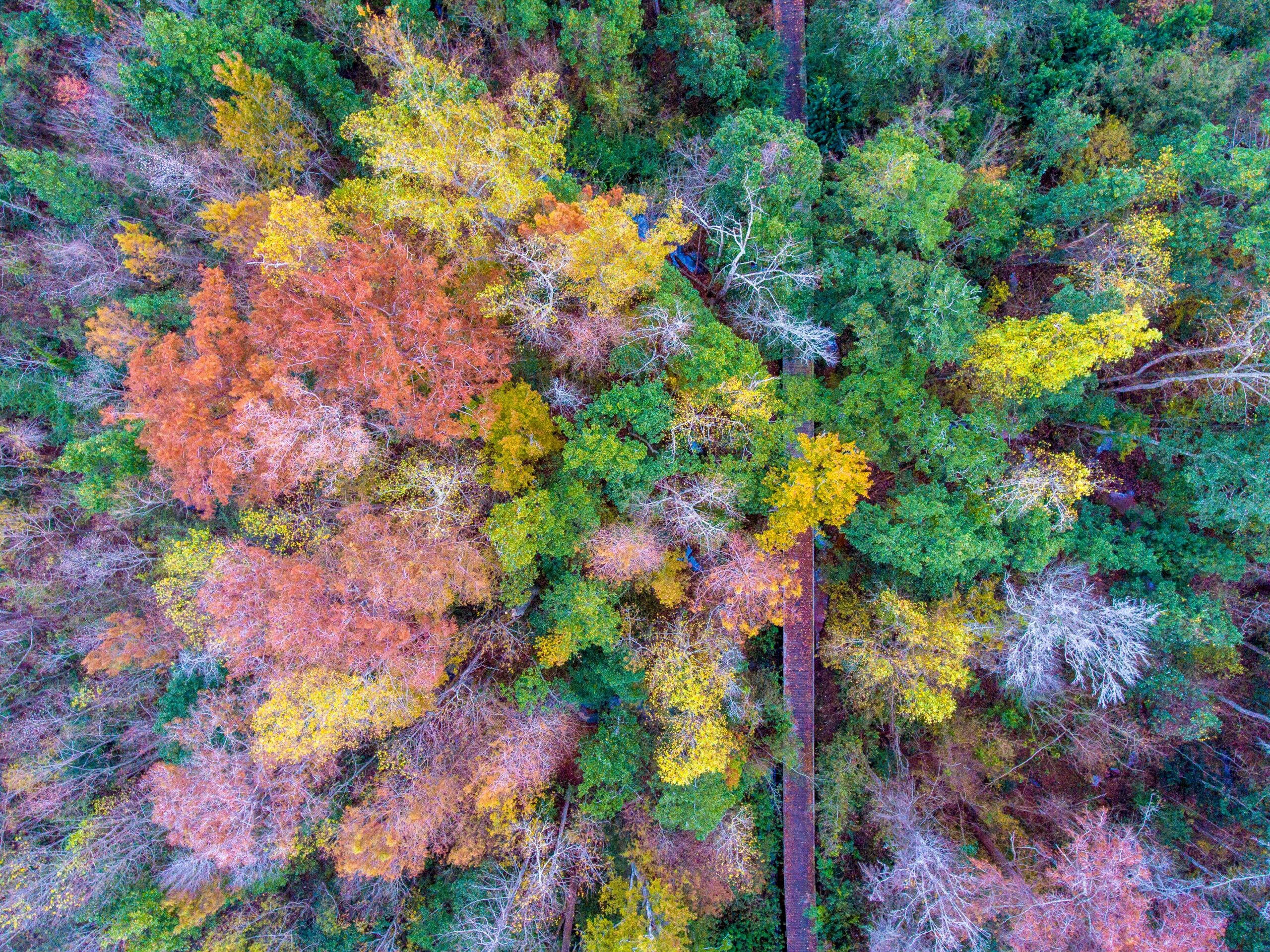
| Tropical Forests: | |
|
 |
|
|
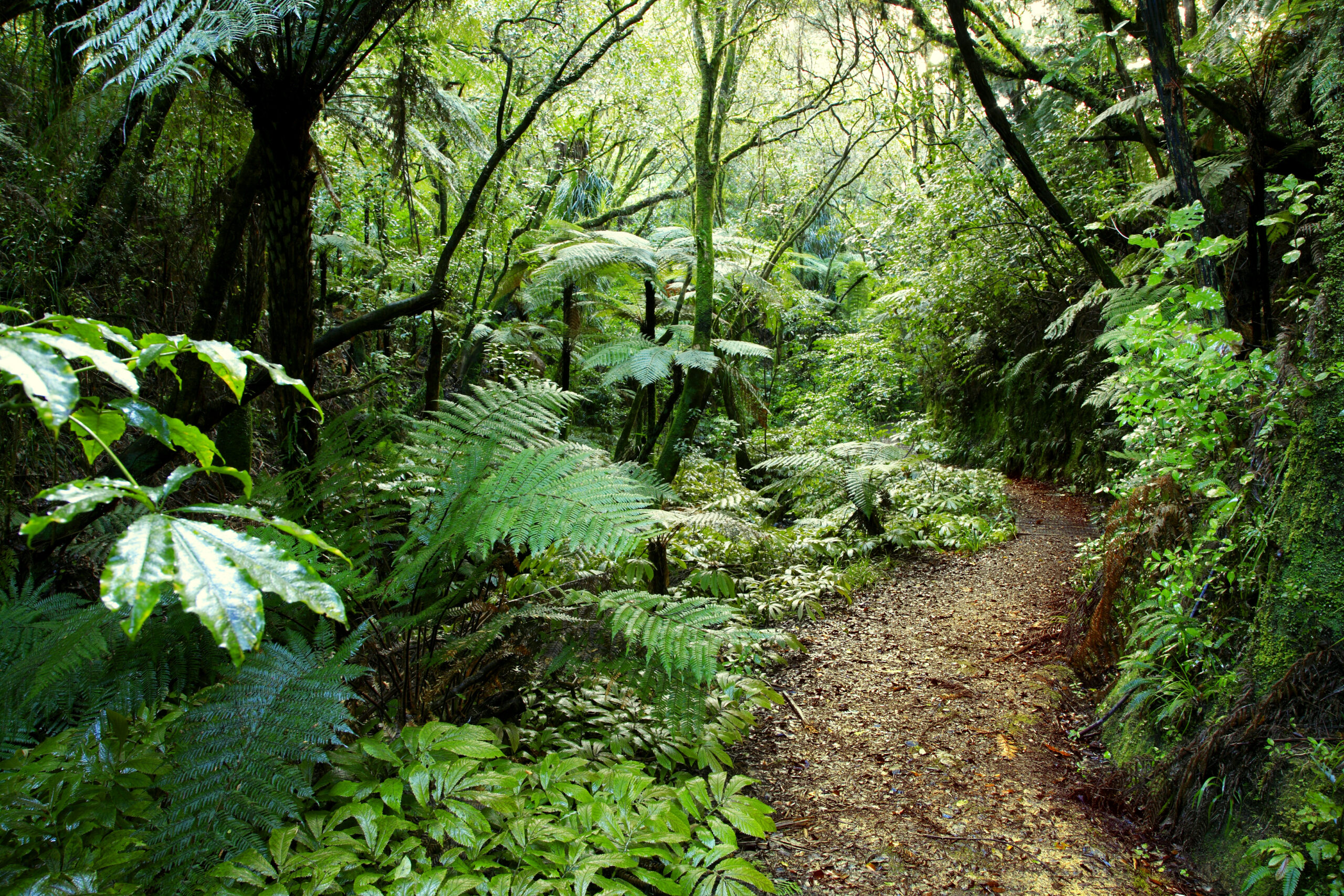
| Temperate Forests: | |
|
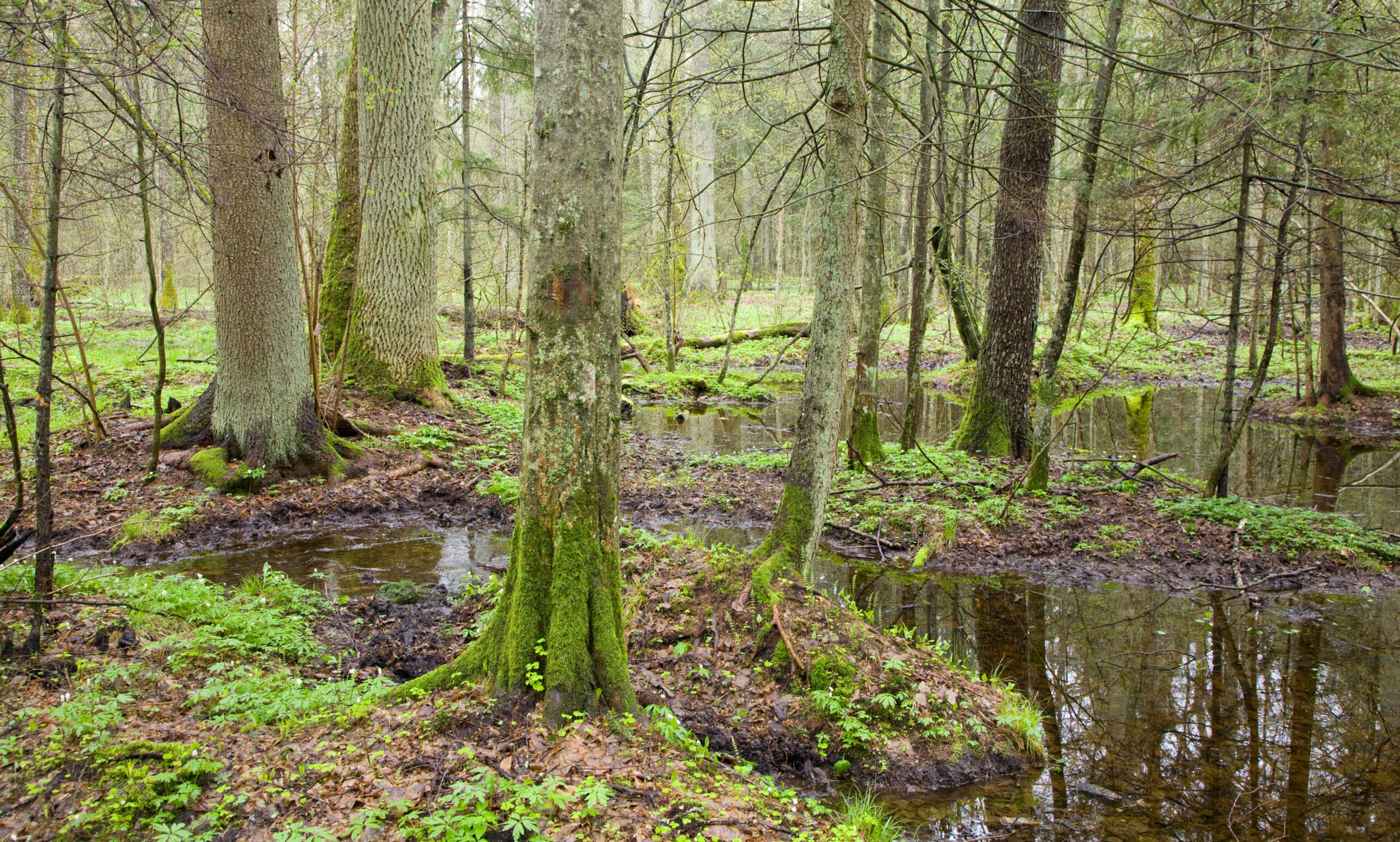 |
|
|
| Boreal Forests: | |
|
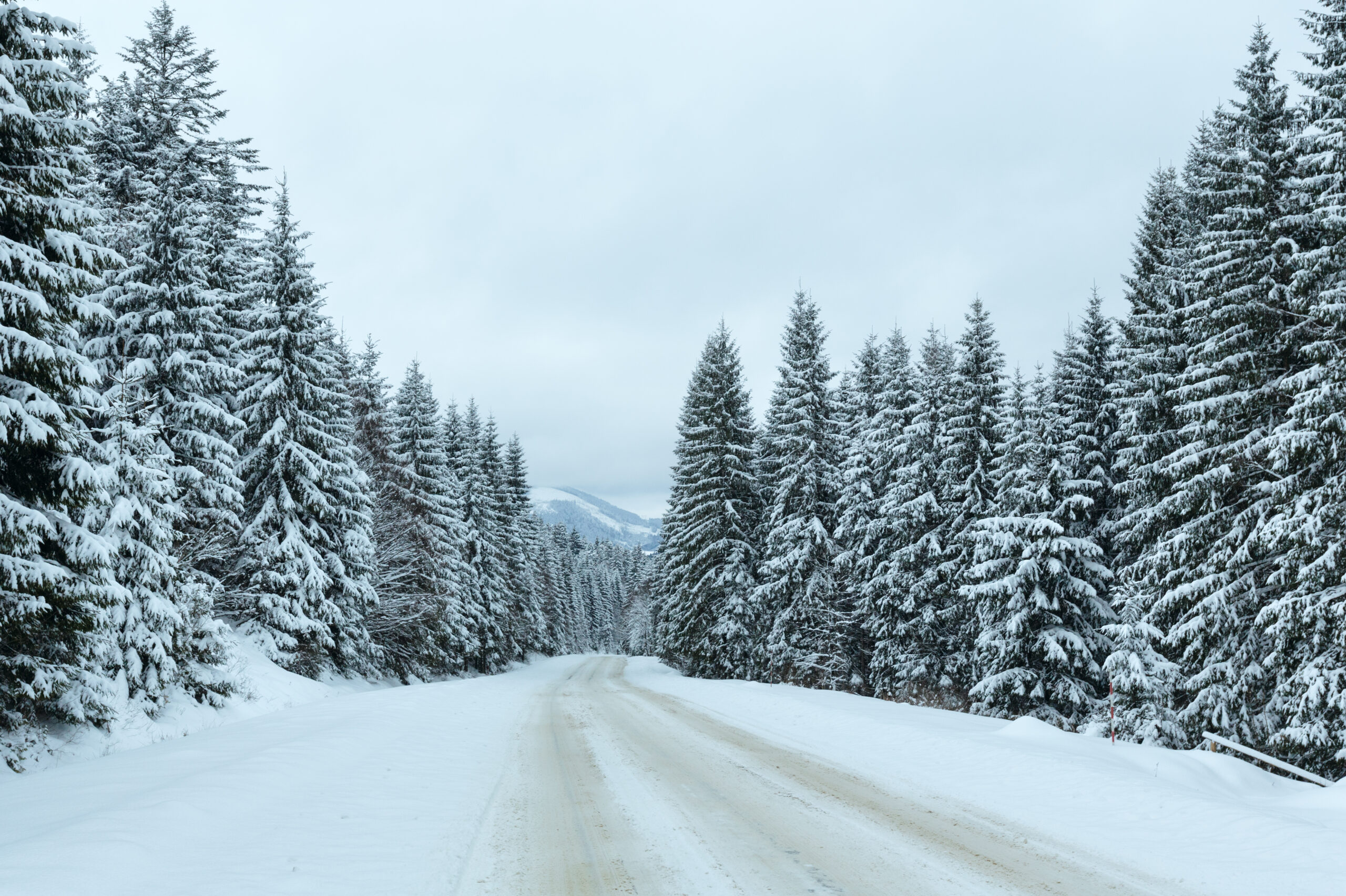 |
|
|
| Forests In Alabama | |||
| Of the 33.5 million acres of land in Alabama, 27 million are forested. That means roughly 70% of the state is covered in trees. These forests contribute to the state's rich biodiversity and also play an important economic role. | |||
| Alabama's Forest Types Alabama's forests are temperate This means they are found between the tropical and boreal regions in areas neither extremely hot nor cold and have four distinct seasons. In spring and summer, plants use sunlight to make food for themselves and grow. In fall and winter growth pauses and leaves begin to dry, change color, and drop from trees. Trees that shed leaves seasonally are called deciduous. Generally speaking, these trees are considered to be hardwoods (trees with broad leaves, true flowers, and seeds enclosed in a fruit or shell). Alabama is also home to trees called conifers. These trees have needles in stead of leaves and cones. They are typically evergreen (stay green year-round). |
||
| A forest with mostly conifers is called a coniferous forest. Generally speaking, these trees are considered to be softwoods (trees with "naked" seeds).
Many of Alabama's forests are called "mixed forests", meaning they have both deciduous trees and conifers. The map shown above shows the distribution of the most dominant forest types across the state, but does not show all of Alabama's forest diversity. Alabama's landscape and forest types have experienced changes throughout history based on use and management practices. Forest types across the state chage as you move across the different ecoregions (shown on the map to the right). |
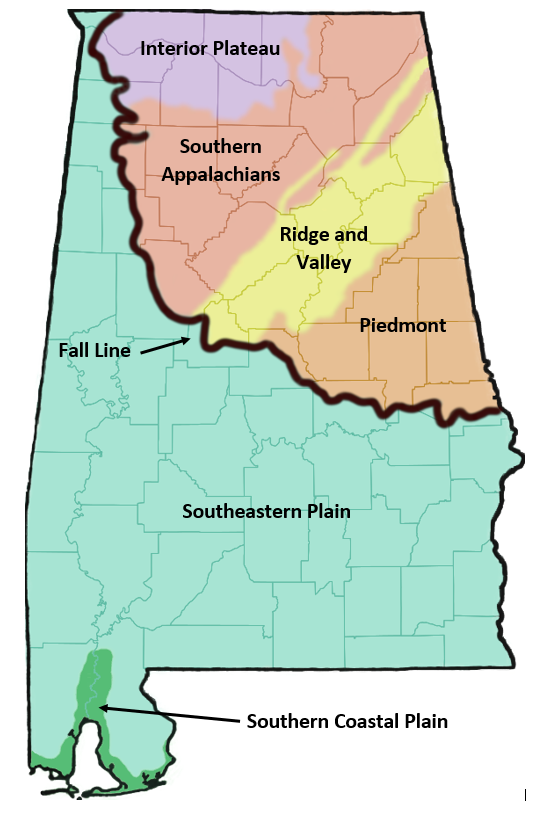 Alabama's Ecoregions
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
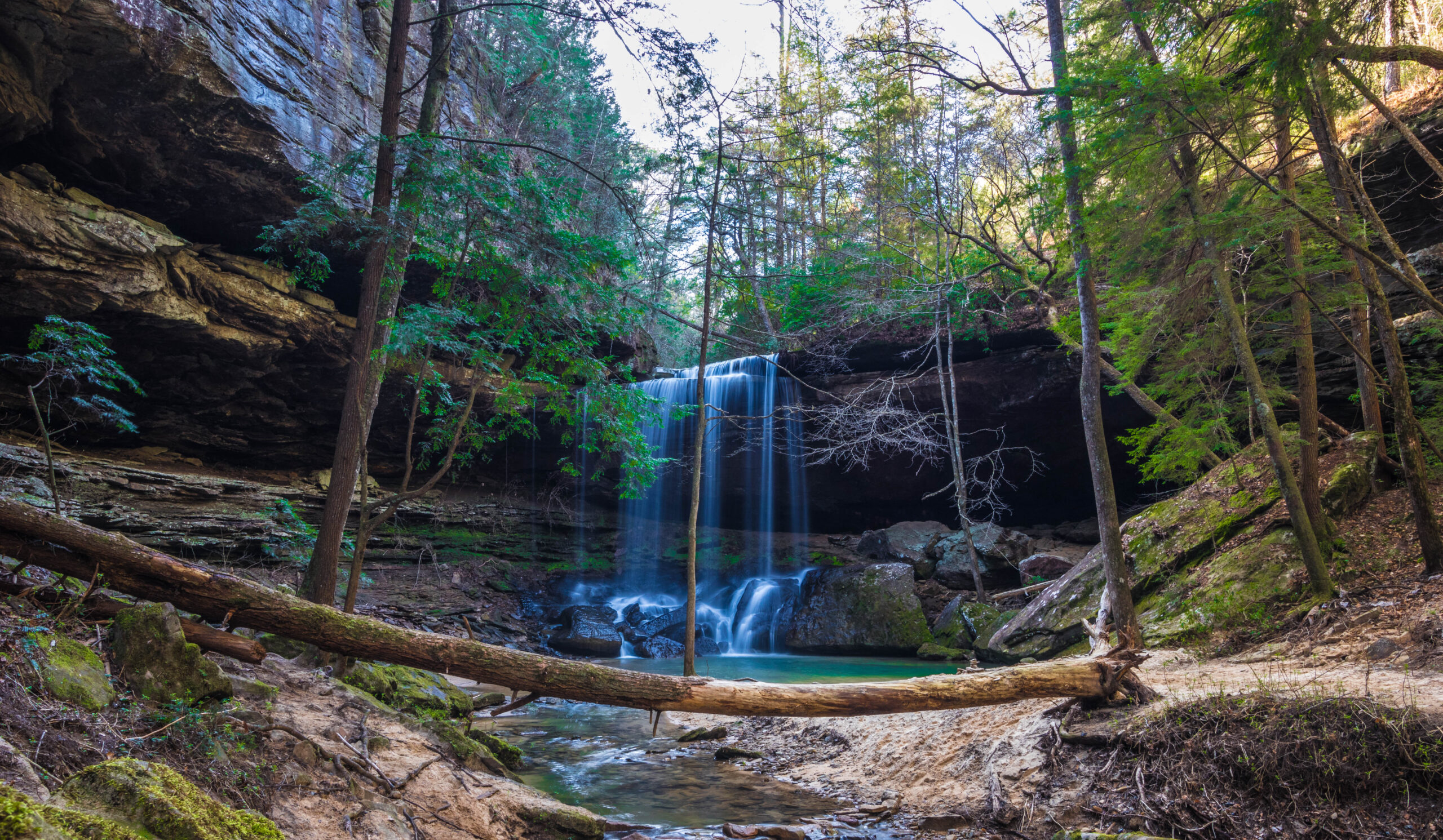
Bankhead National Forest
|
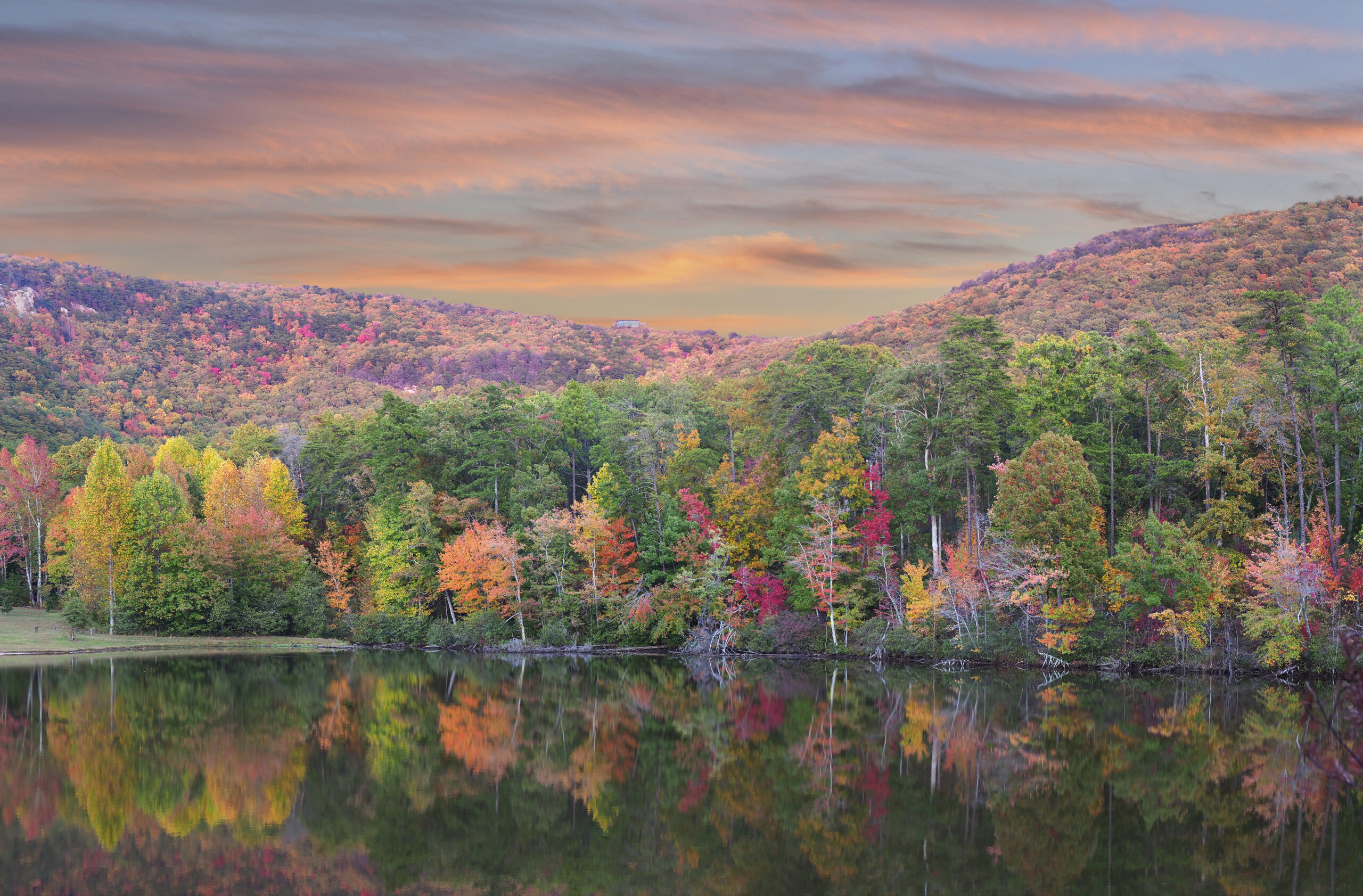
Talladega National Forest
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
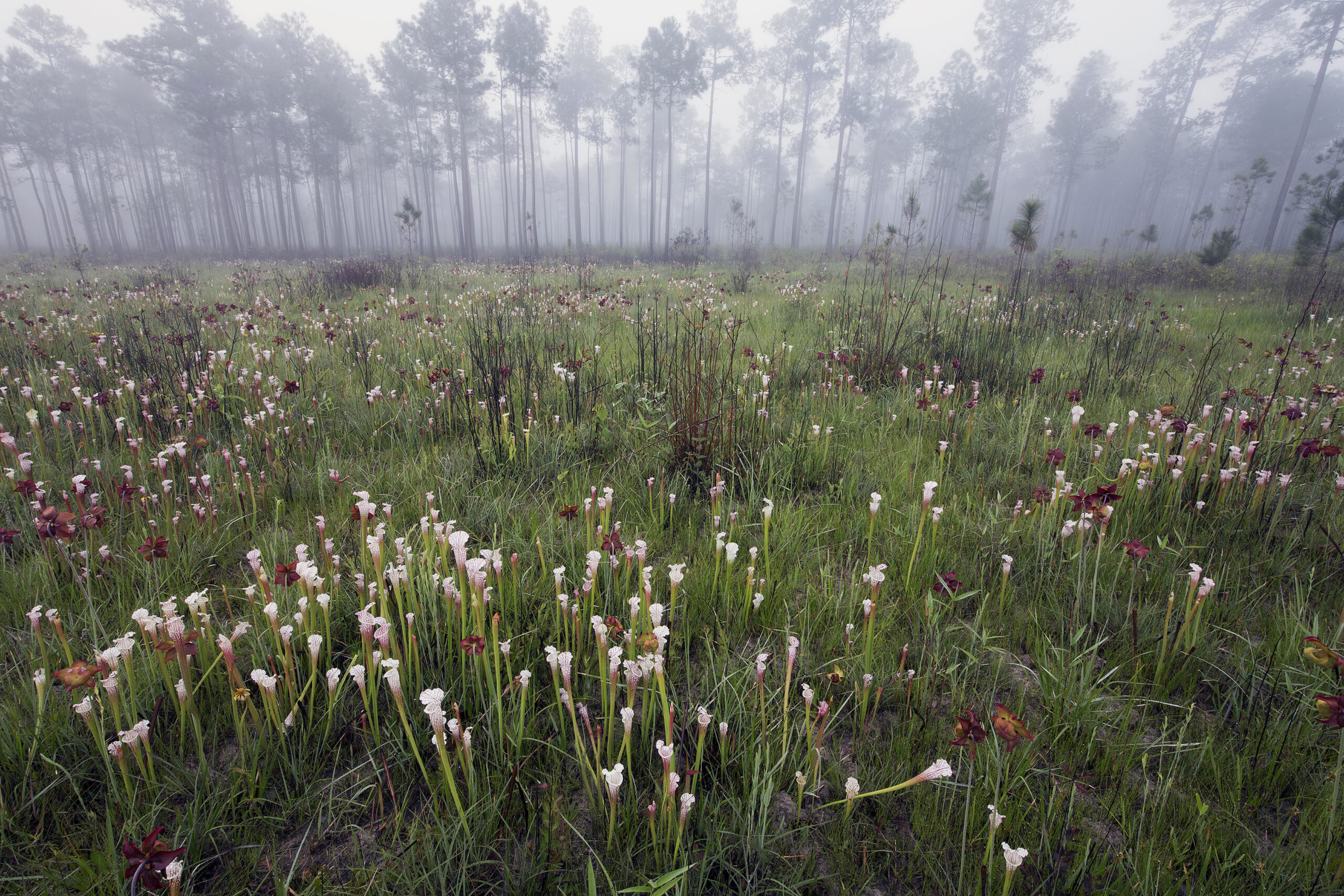
Conecuh National Forest
|
Tuskegee National Forest
|
| Importance of Forests | |
|
Forests provide habitat for wildlife.
|
|
|
|
|
Forests also help prevent erosion.
|
|
|
Forests are excellent at storing greenhouse gases.
|
|
|
|
|
Humans also depend on the forest economically.
|
|
|
Right now, forests across the world are at risk for many reasons. The biggest reasons include:
The loss of forests across the world has and will continue to impact wildlife and humans, but scientists and conservationists across the world are making great strides in slowing down loss and increasing restoration efforts.
|
|
SOURCES USED FOR THIS PAGE:

Encyclopedia of Alabama
Forest Regions of Alabama National Forests of Alabama |
 National Geographic
Forest Biome Controlled Burning |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
Website Design and Digital Marketing by