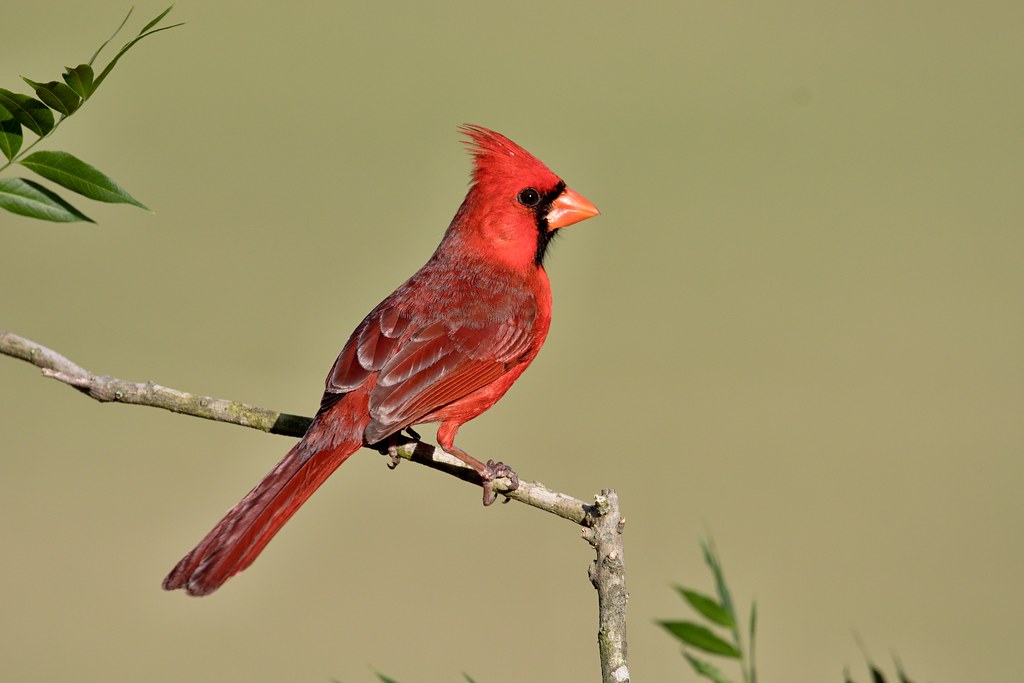
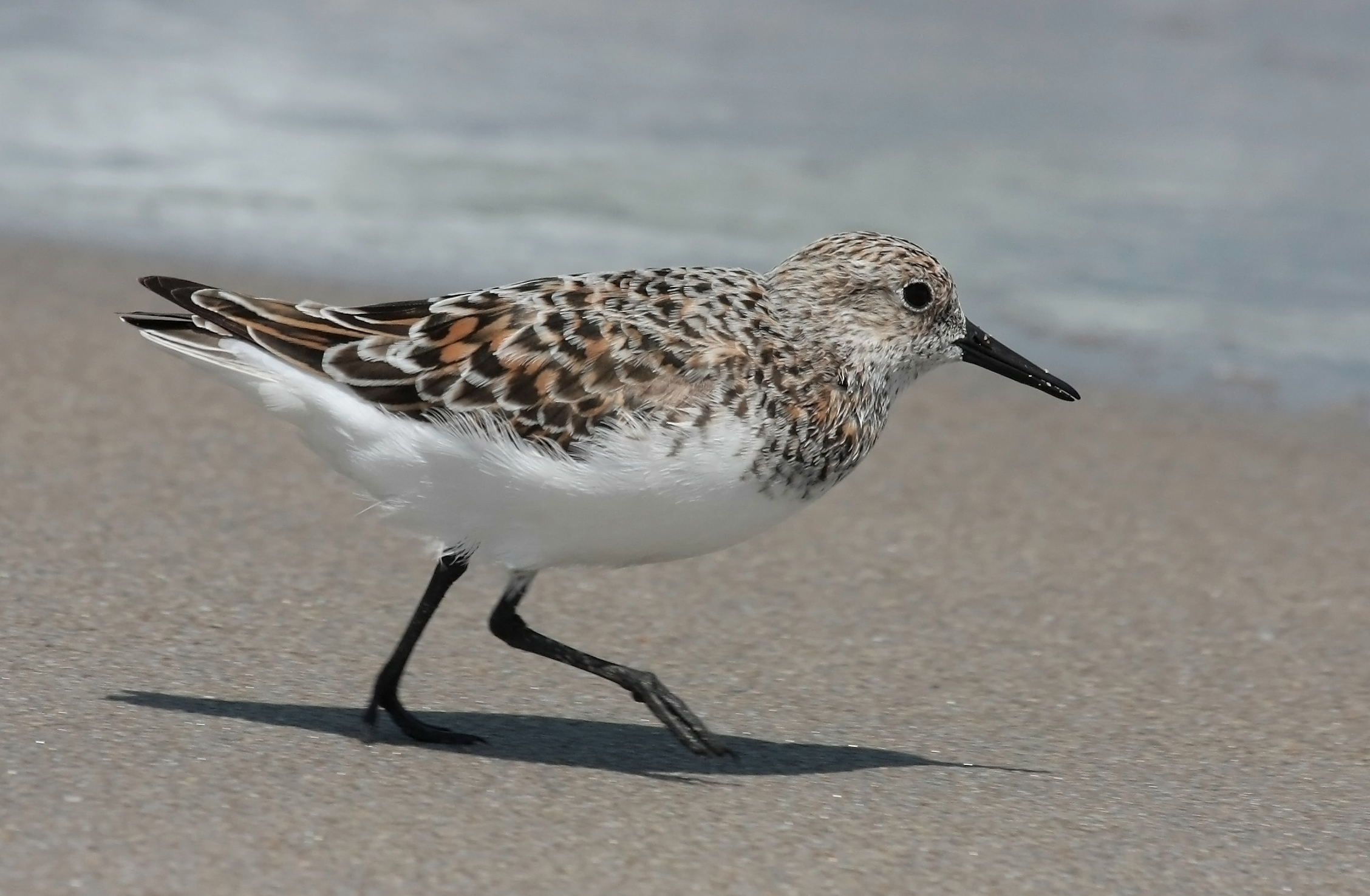
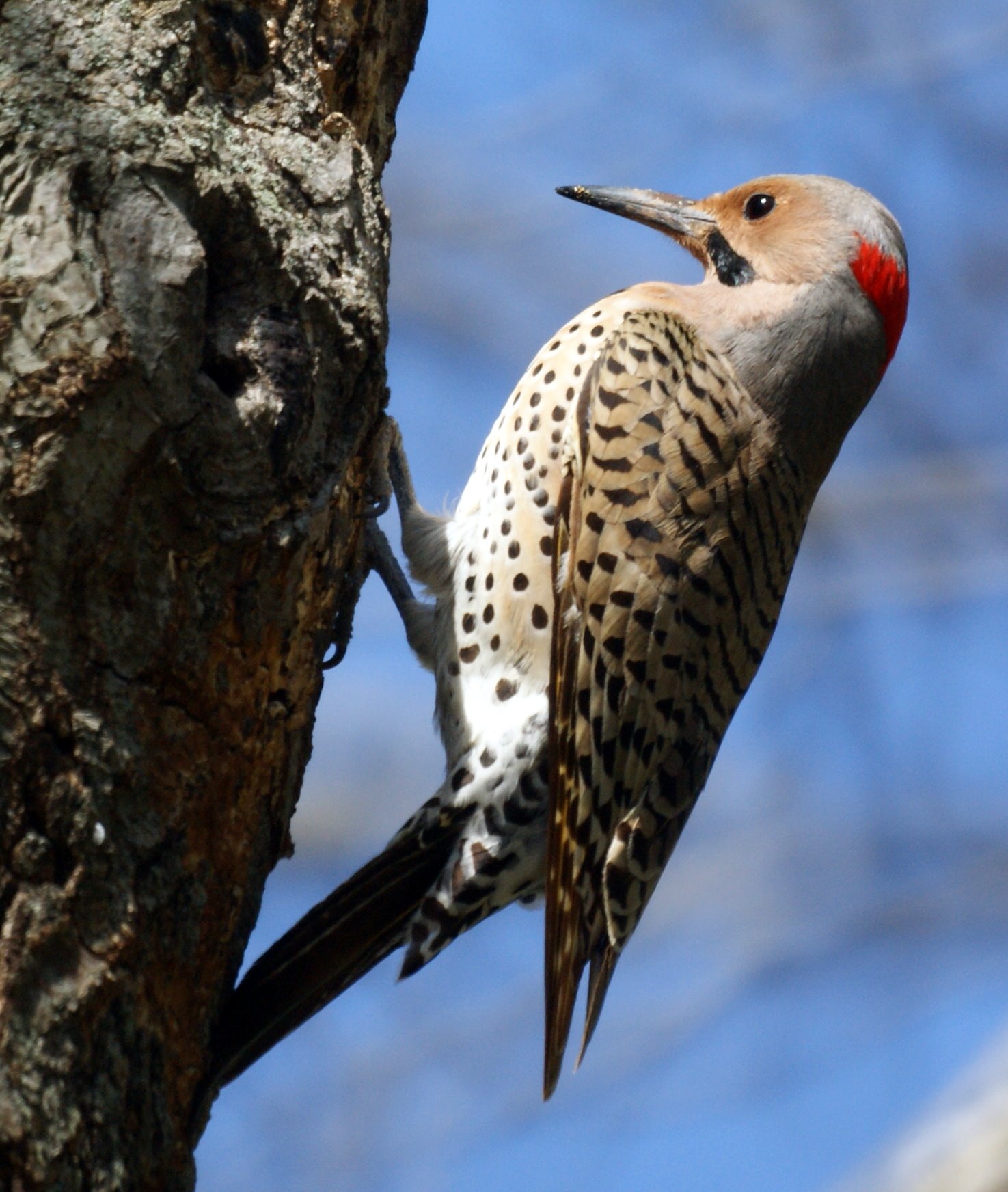
Investigate Alabama's Native Wildlife
Investigate Alabama's Native Wildlife
Alabama is ranked 4th place for most biodiversity in the United States and has more biodiversity than any other state east of the Mississippi River!
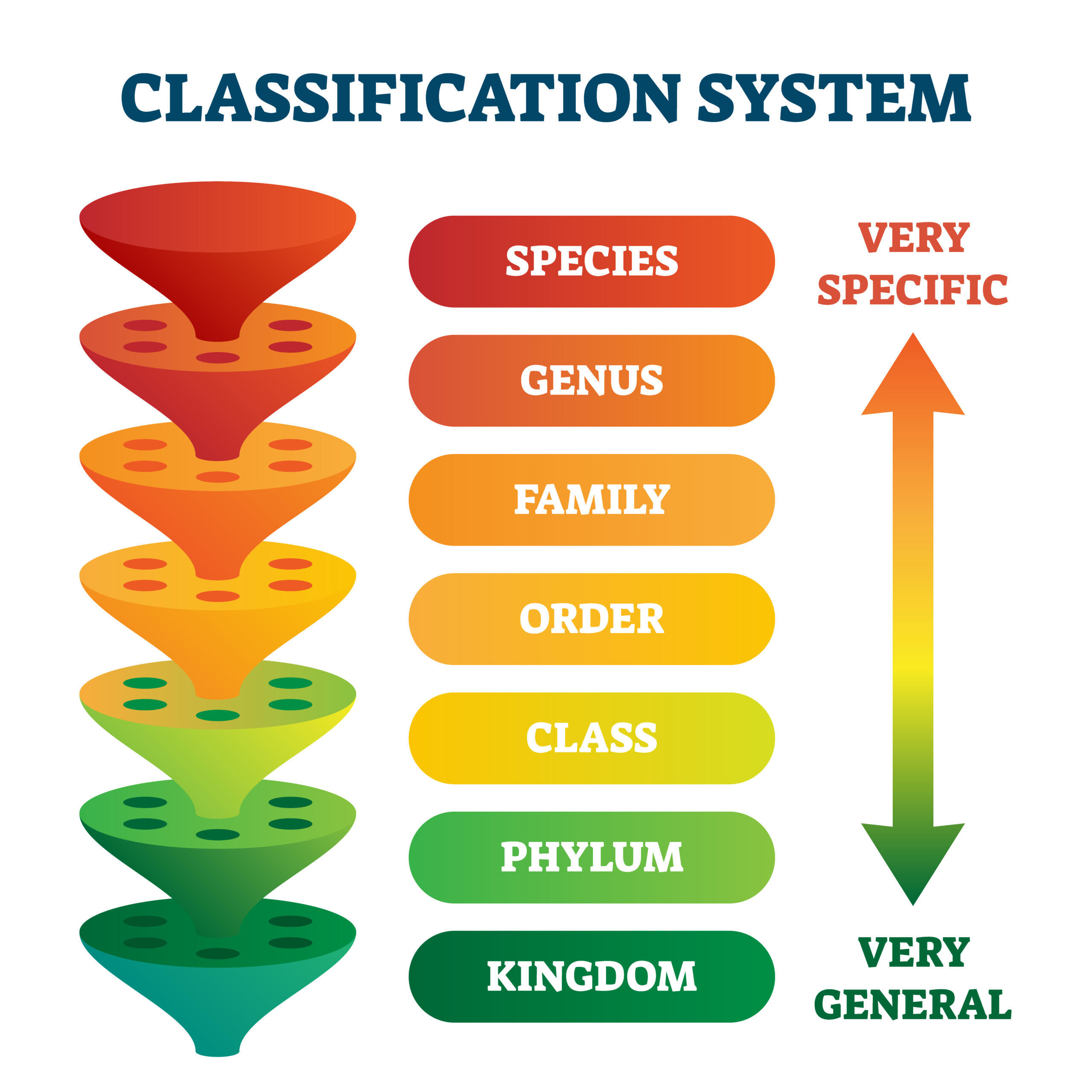 The animals found in Alabama and across the world can be classified into different groups like the ones on this page. Classification is the process of organizing organisms into groups based on similarities. Scientists use basic traits to group organisms into taxonomic classes (groups).
The animals found in Alabama and across the world can be classified into different groups like the ones on this page. Classification is the process of organizing organisms into groups based on similarities. Scientists use basic traits to group organisms into taxonomic classes (groups).
These groupings start broad and are further broken down into more specific groups within the larger group. A species is the most specific category within the classification system.
For a taxonomic classification chart comparing key traits of common backyard wildlife, click here!
| Click on the topics below to learn more about the common groups of organisms found in Alabama! |
||
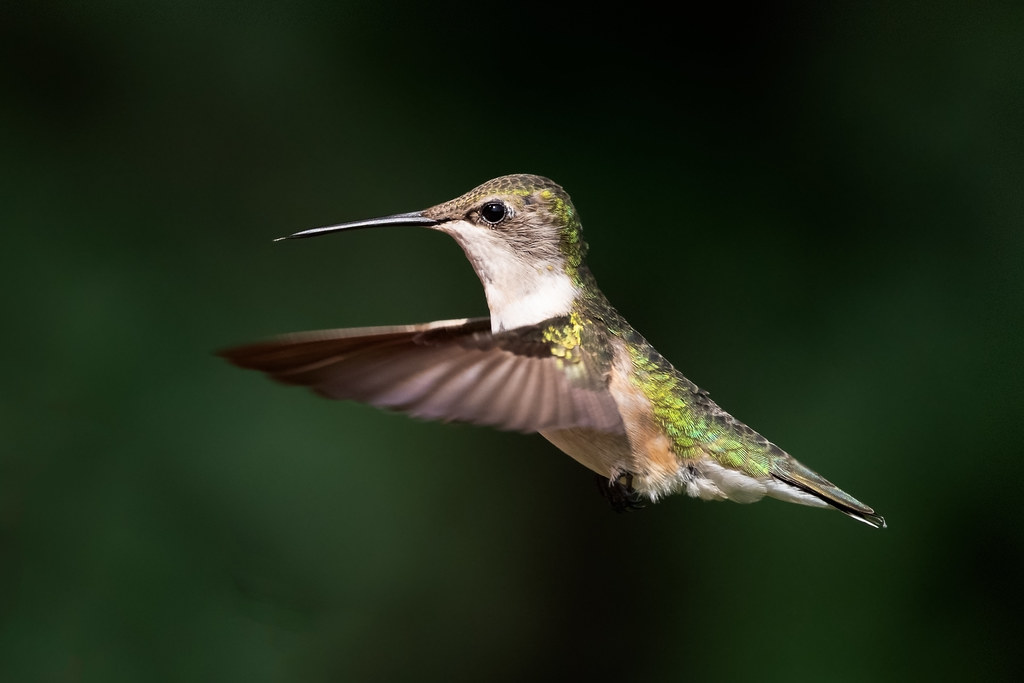
| Amphibians | Birds | Fish |
| Mammals | Reptiles | Arthropods |
| To learn more about animals within these classes that you may see in your outdoor classroom, click here! |
||
| Amphibians | ||||
| Classification: | ||||
|
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
|
|
|||
| Amphibian Characteristics: | ||||
|
||||
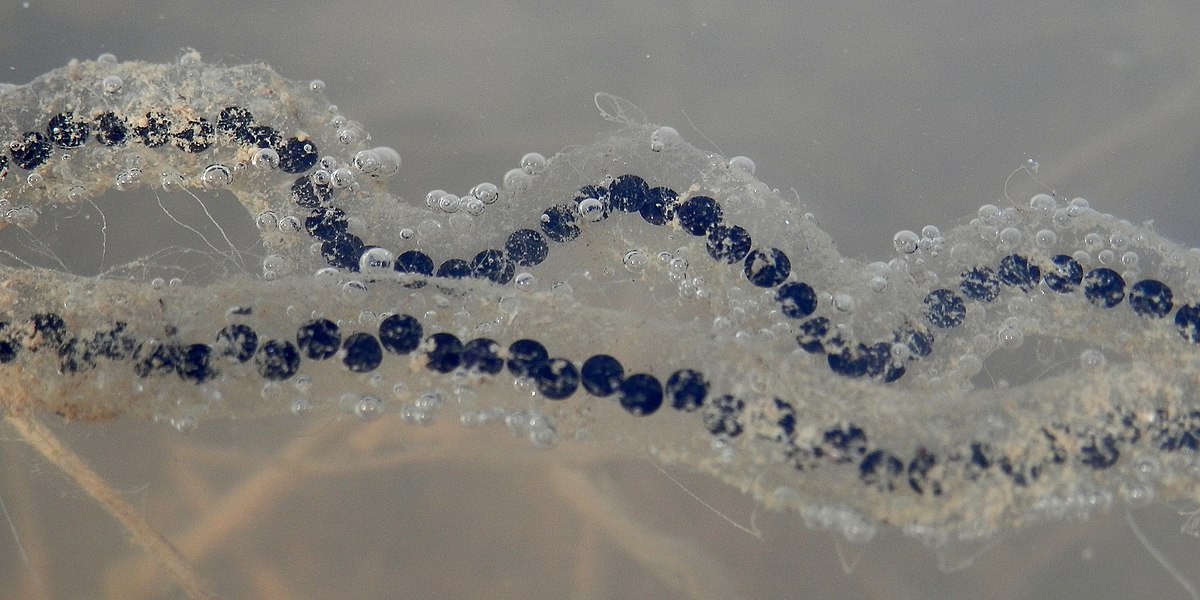
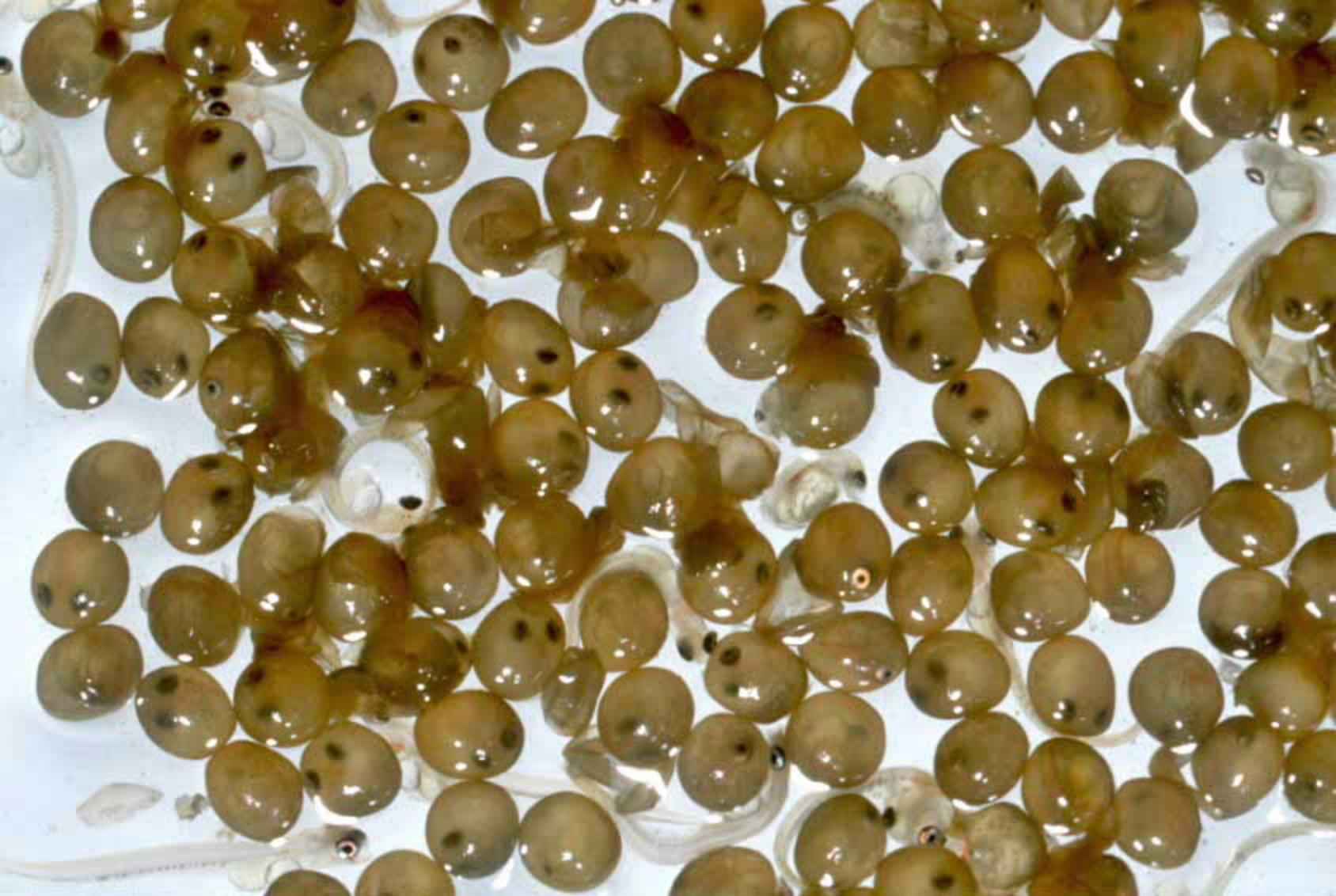
|
American Toad Egges
Ryan Hodnett – Wikimedia Click image to enlarge it |
|||
| Common Groups of Amphibians: | ||||
| Frogs: | Salamanders: | |||
|
American Bullfrog |
Slimy Salamander |
|||
|
|
|||
| Alabama Amphibian Diversity: | ||||
| 30 species of frogs
43 species of salamanders The southeastern United States has more amphibian diversity than anywhere else in the world! |
Amphibian Diversity |
|||
| Notable Amphibians of Alabama: | ||||
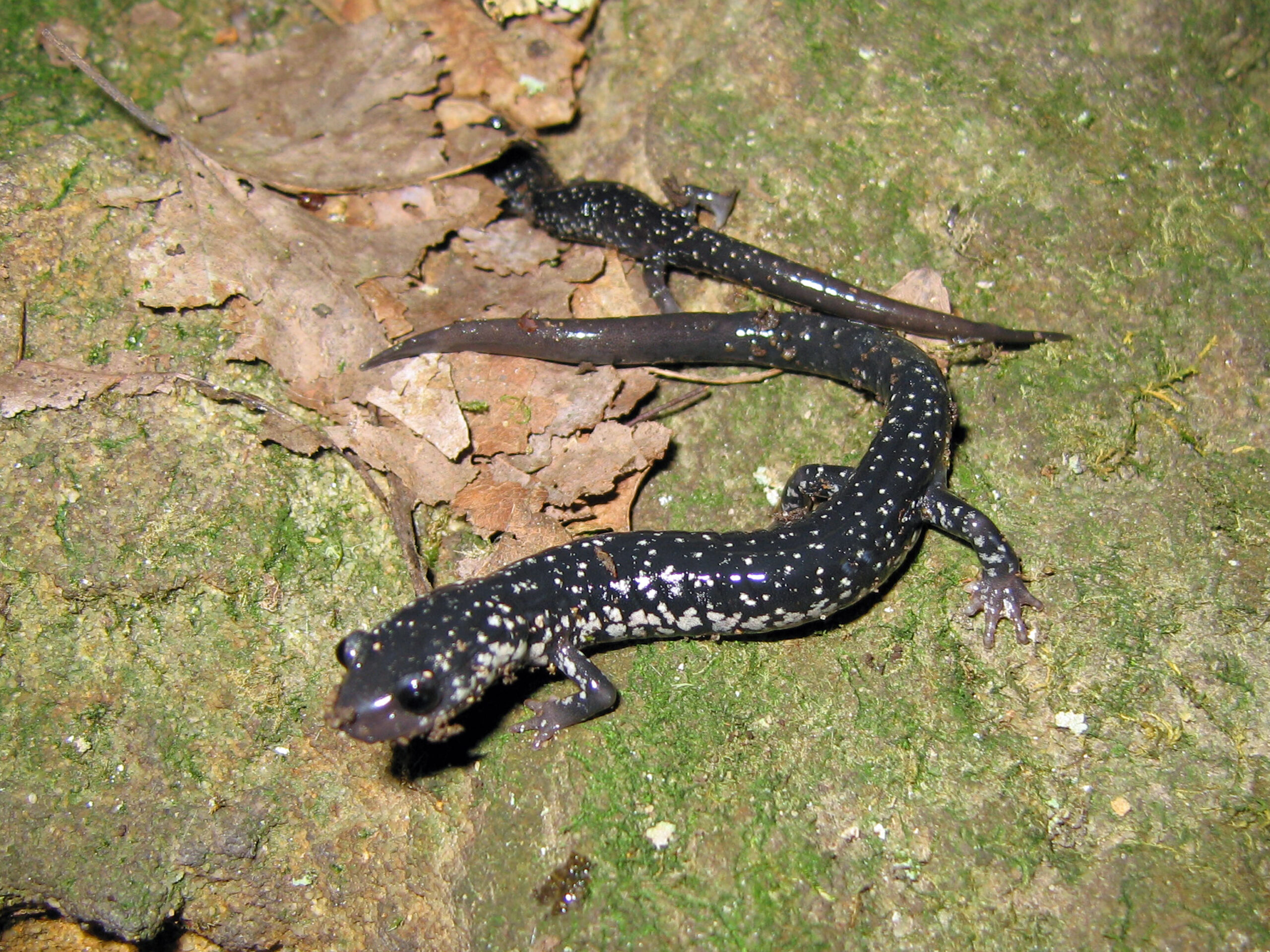
| Red Hills Salamander
The Red Hills salamander is only found in Alabama! The term for when an organism is native to and only found in one place is called "endemic" or "endemism". |
Red Hills Salamander
flickr – John P. Clare Click on image to enlarge it |
|||
| The Red Hills salamander is Alabama's state amphibian. | ||||
| Fish | ||
| Classification: | ||
|
Kingdom
Animalia (animals)
Phylum Class
Different types of fish as classified into different classes. The three main categories are jawless fish, fish with a cartilage-like (soft) skeleton, and bony fish.
|
||
| Fish Characteristics: | ||
|
Salmon Eggs
Pixnio – USFWS Click on image to enlarge it |
|
| Common Groups of Fish: | ||
| Sharks, Rays, and Chimaeras: | Bony Fishes: | |
|
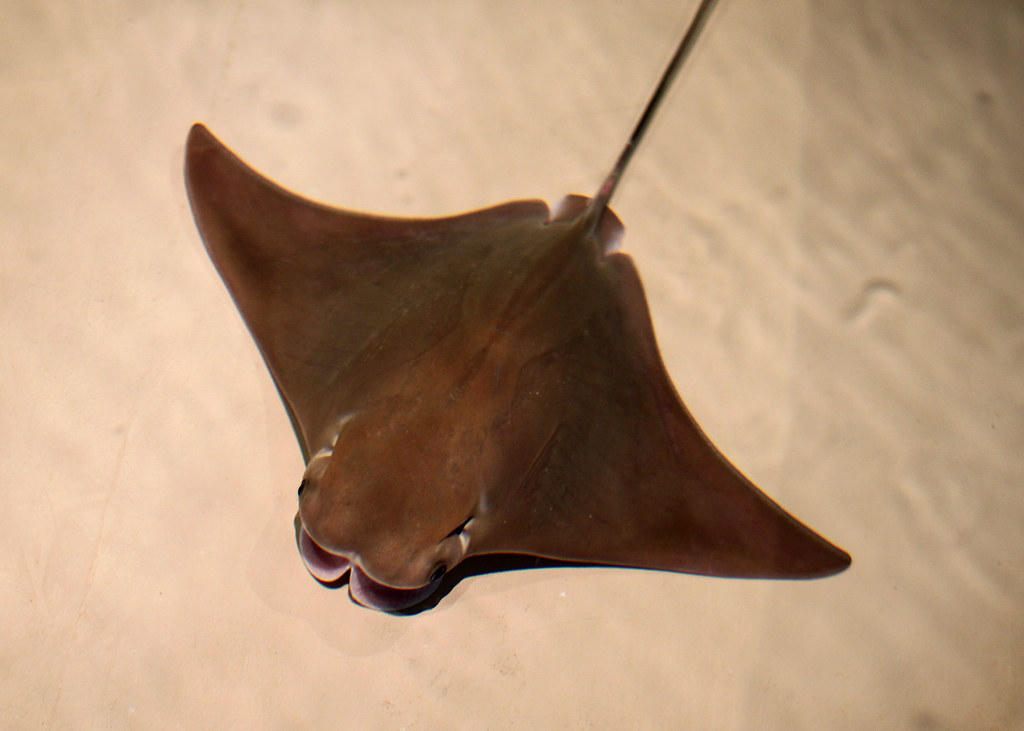
Cownose Ray
flickr – MR.TinDC Click on image to enlarge it |
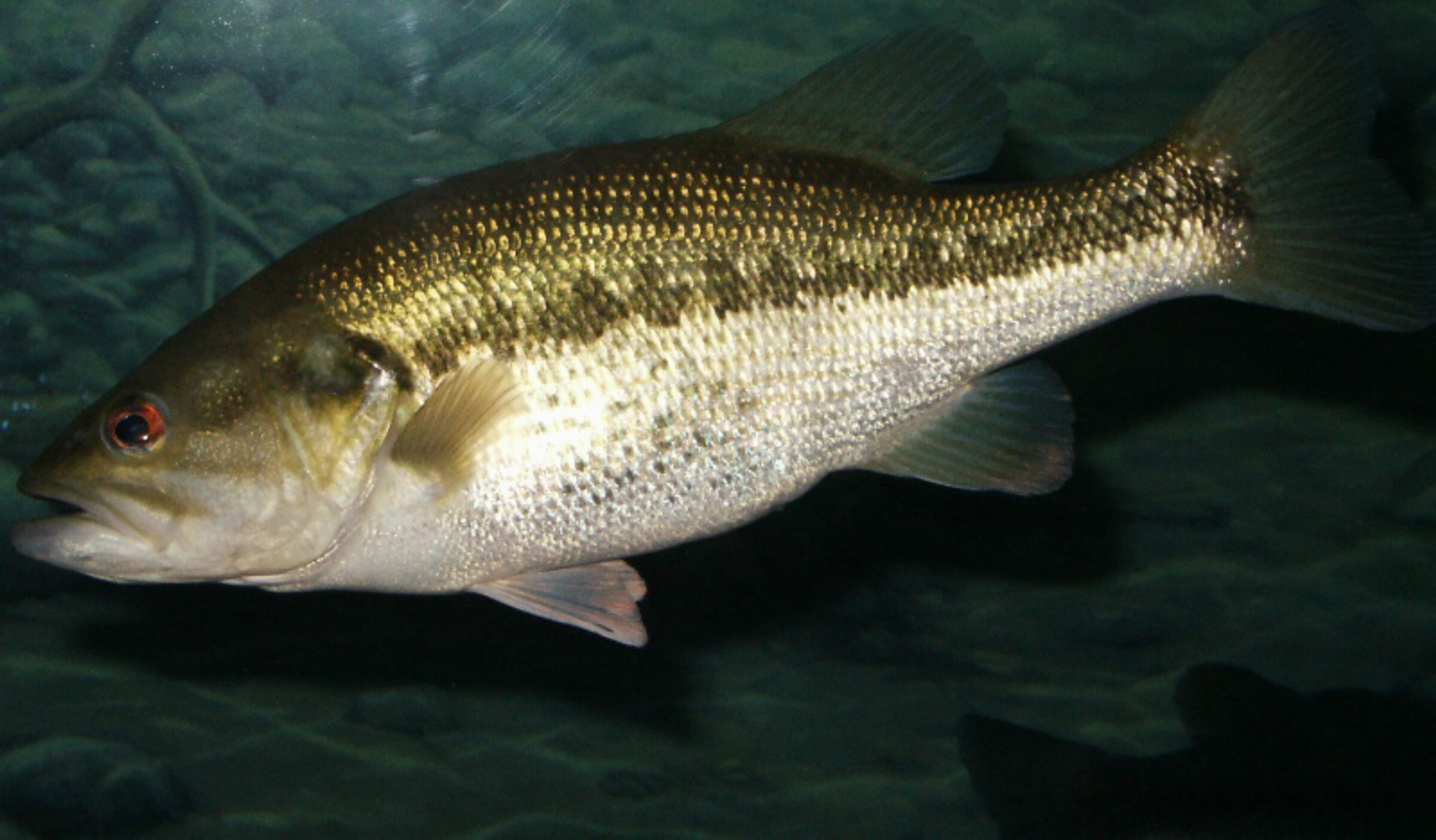
Largemouth Bass
Wikimedia – Robert Pos Click on image to enlarge it |
|
|
|
|
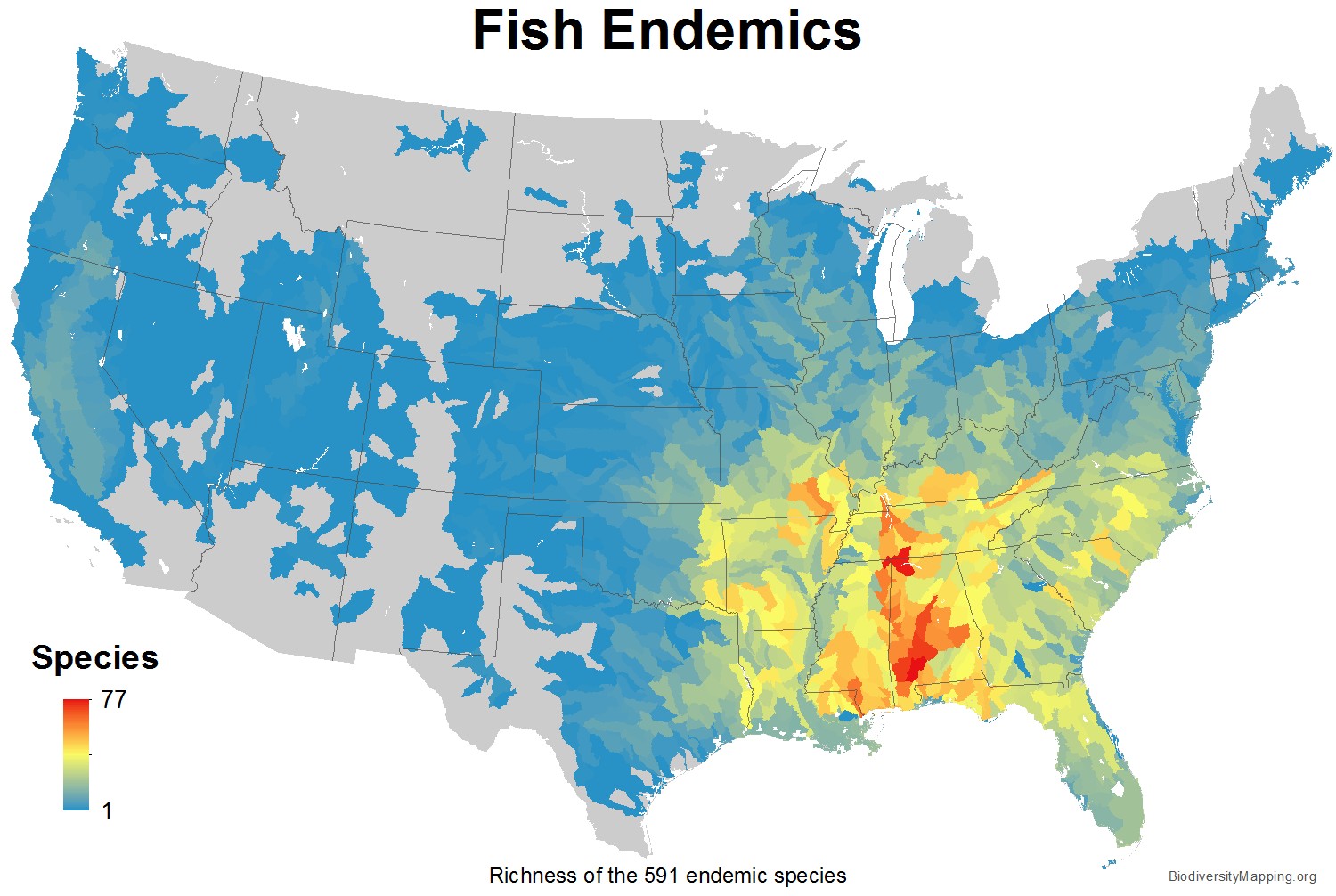
| Alabama Fish Diversity: | ||
|
450 species of fish
#1 for diversity in the United States!
38% of the North American fish species are native to Alabama
|
Fish Diversity |
|
| Notable Fish of Alabama: | ||
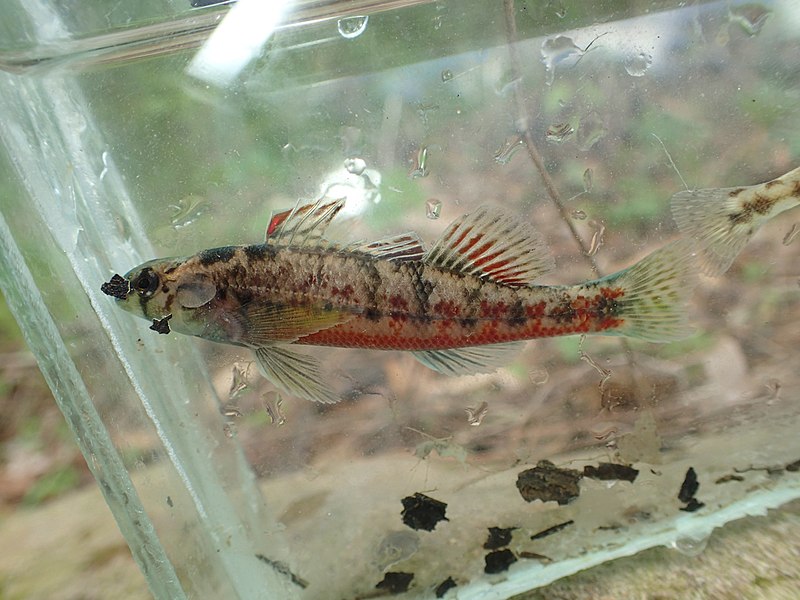
| Vermilion Darter
The vermilion darter can only be found in Turkey Creek, a side stream that flows into the Balck Warrior River system in Jefferson County. The vermilion darter is a yellowish olive colored fish with greenish stripes on the back and green and maroon spots along its sides. The underside of the fish is a bright reddish scarlet color called vermilion. |
Vermilion Darter |
|
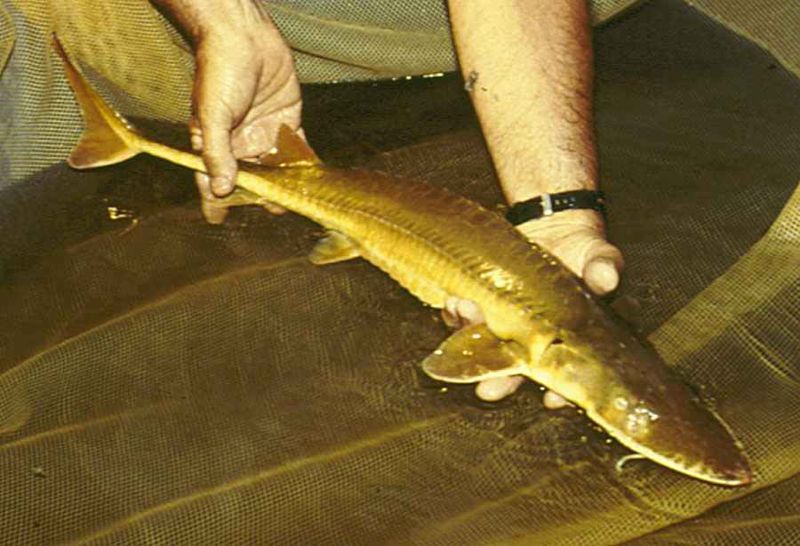
| Alabama Sturgeon
Tha Alabama Sturgeon is only found in Alabama in the Mobile basin. It has been found in deep, fast moving waters with a rocky or sandy bottom. It can grow up to around 2.5 feet in length and has an elongated snout with four feelers hanging below the mouth. The back and fins are brownish orange, the sides are yellow, and the underside is cream colored. |
Alabama Sturgeon |
|
|
Fish Endemics |
||
| Mammals | ||
| Classification: | ||
|
Kingdom
Animalia (animals)
Phylum Class
Mammalia (Mammals)
|
||
| Mammal Characteristics: | ||
|
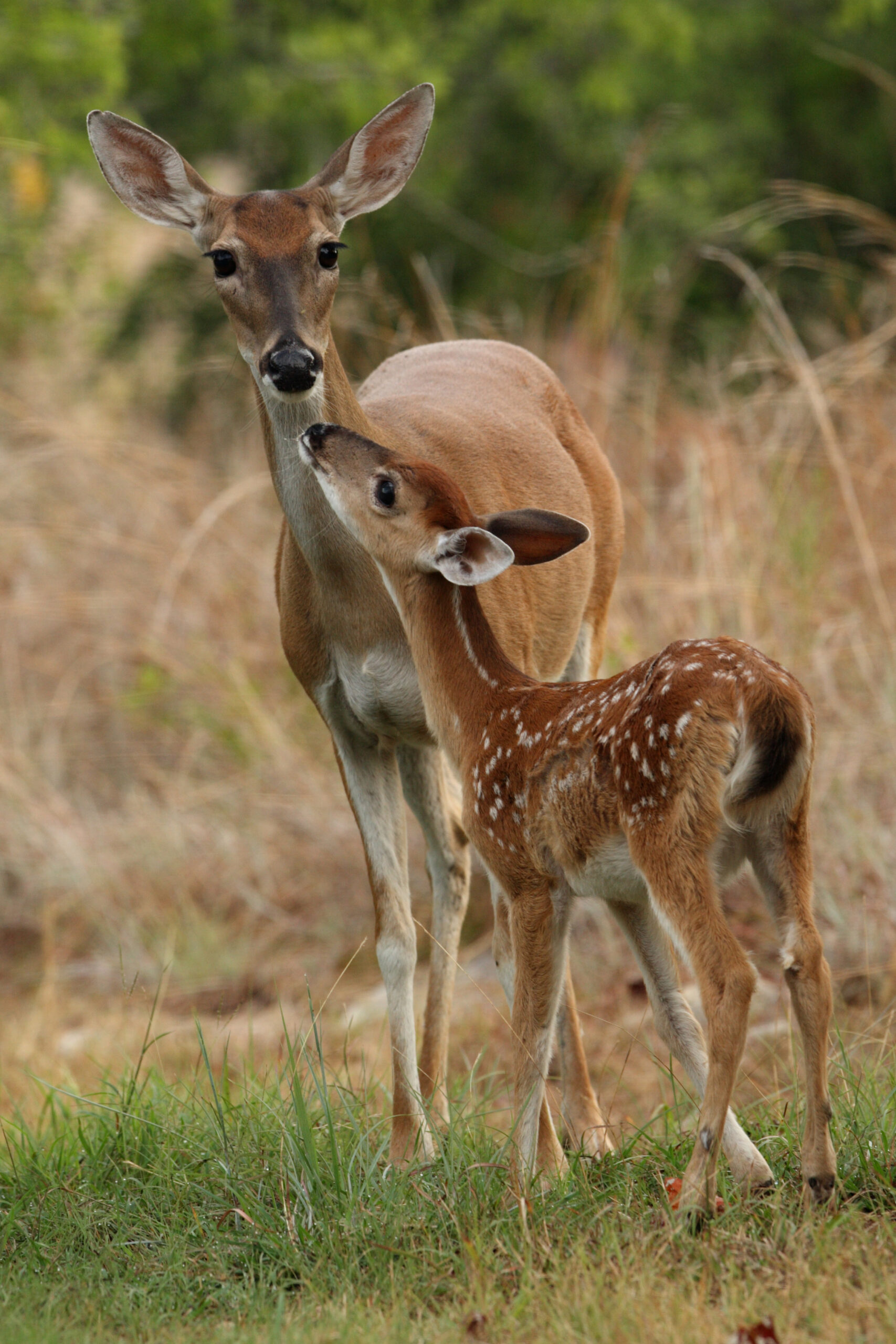
White Tailed Deer and Baby
Dreamstime Click on image to enlarge it |
|
| Mammals in Alabama: | ||
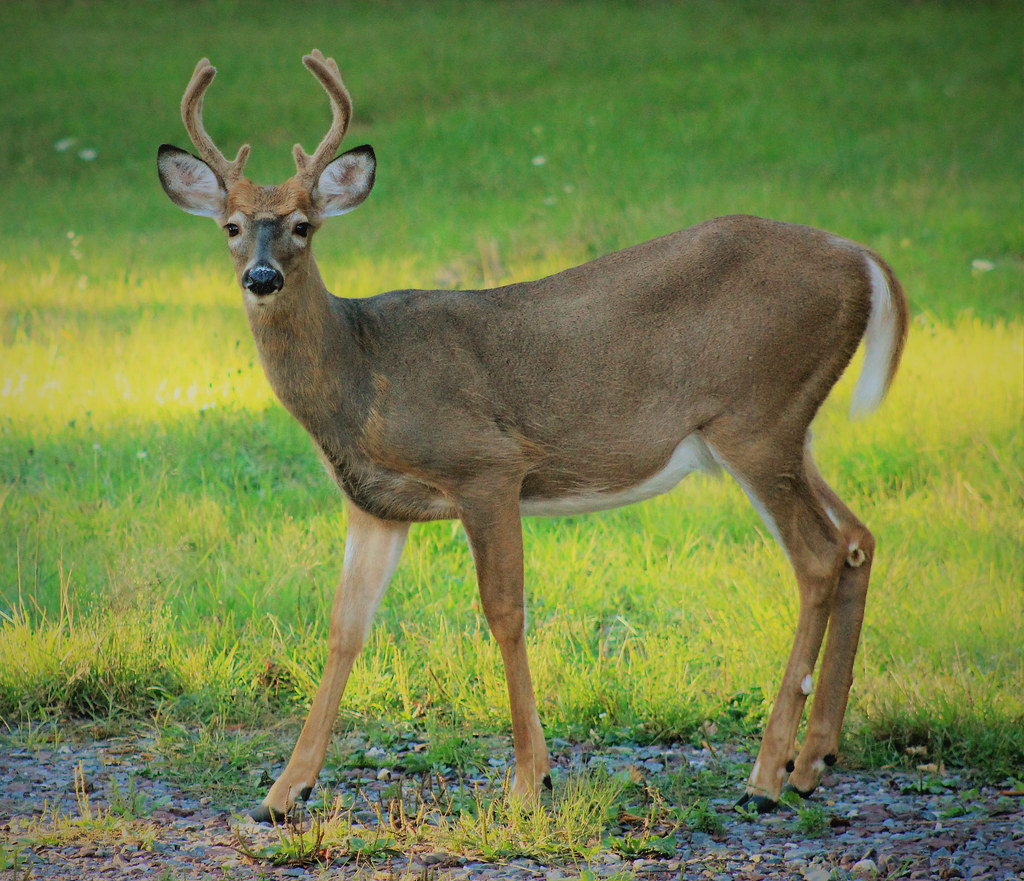
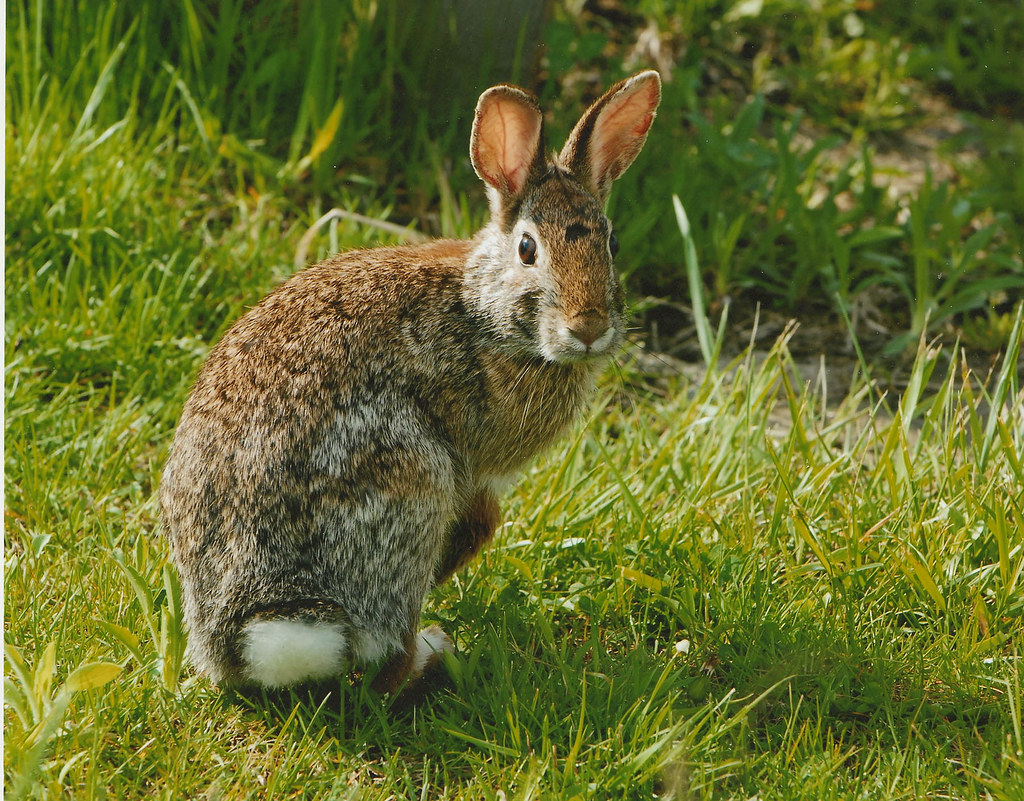
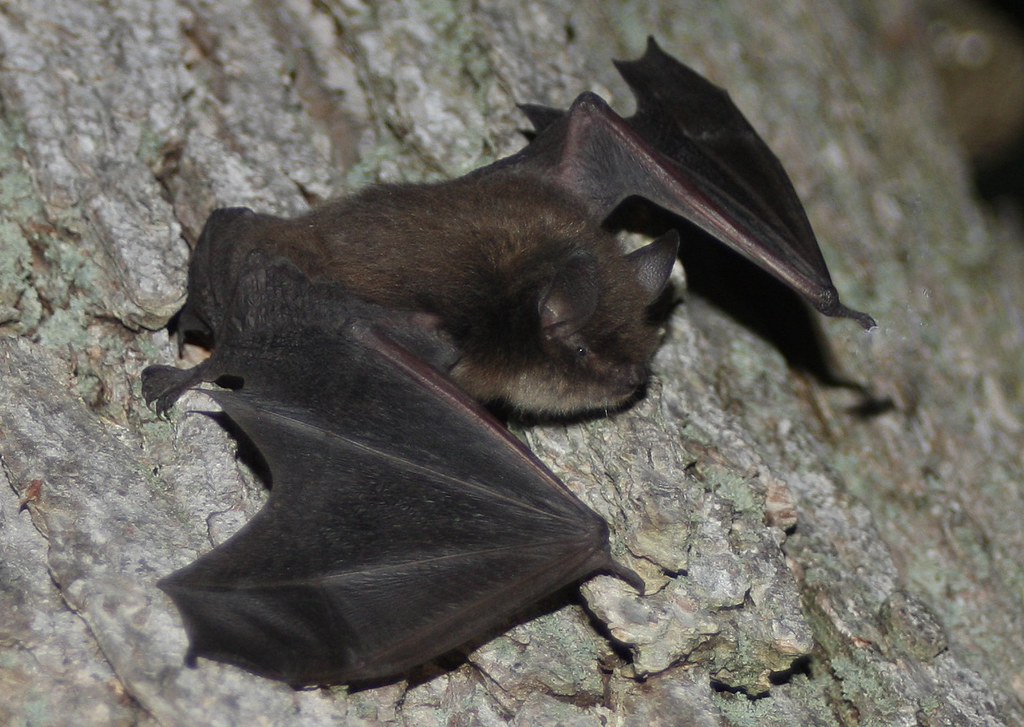
| Alabama's various habitats provide homes for a diversity of mammals including rodents, foxes, bats, deer, and rabbits. | ||
| Deer | Rabbits | |
|
White Tailed Deer
flickr – Nicholas_T Click on image to enlarge it |
Eastern Cottontail
flickr – U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Northeast Region Click on image to enlarge it |
|
|
|
|
| Bats | Coyotes and Foxes | |
|
Little Brown Bat
flickr – J.N. Stuart Click on image to enlarge it |
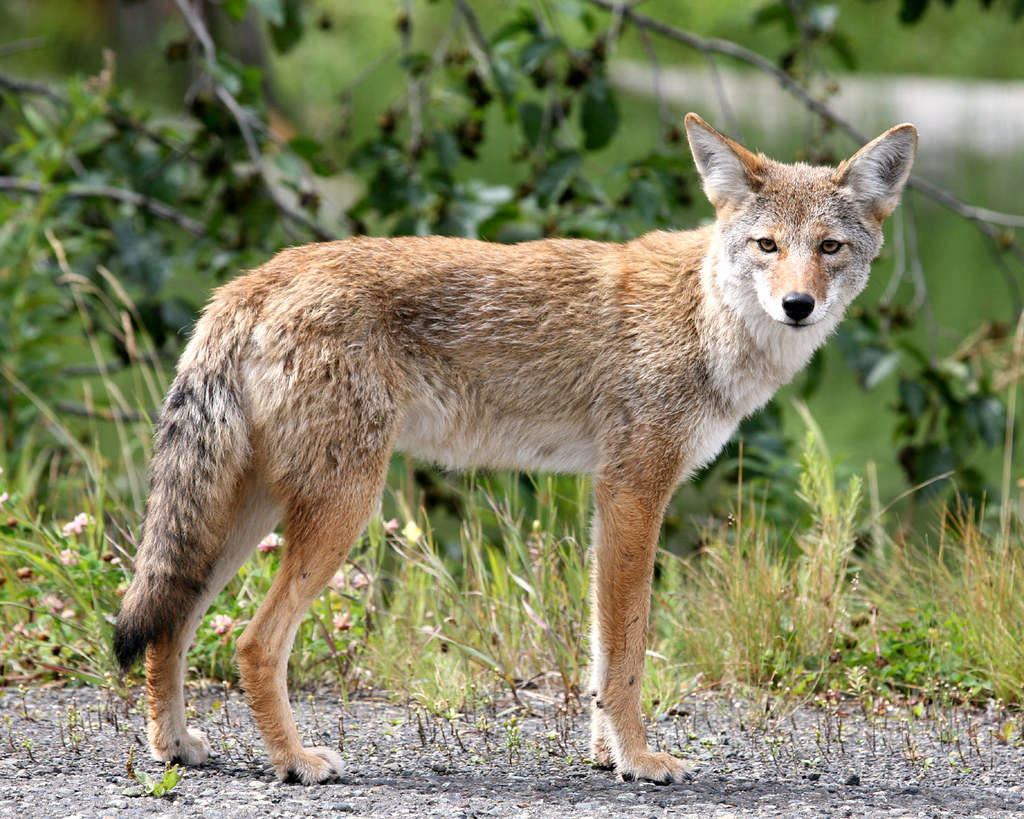
Coyote
flickr – Jitze Couperus Click on image to enlarge it |
|
|
|
|
| Alabama Mammal Diversity: | ||
|
62 native species
22 species of rodents
16 species of bats
11 species of carnivores (meat eaters) |
||
| Notable Mammals of Alabama: | ||
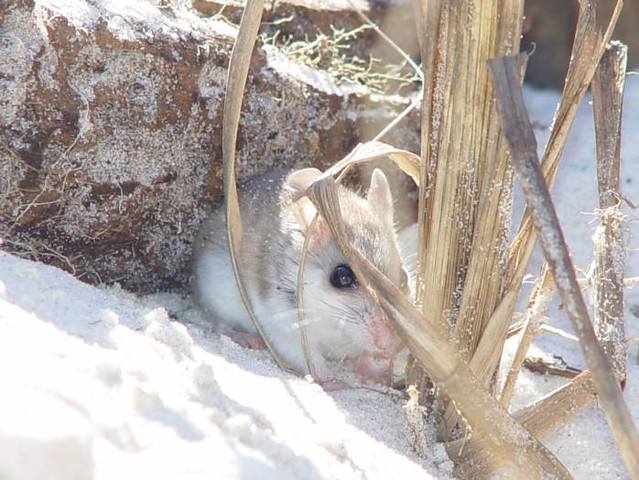
| Alabama Beach Mouse
The Alabama beach mouse is a small field mouse that lives in coastal sand dune habitats. They burrow tunnels in the sand and are active at night. They are characterized by having light colored fur, large ears, and large, dark eyes. This species is only found near the Alabama coastline. |
Alabama Beach Mouse |
|
| American Black Bear
The black bear is Alabama's state mammal and is the only species of bear found in Alabama. They can be found in the forests in the north eastern part of the state as well as in areas north of Mobile. Black bears range in color from black to brown or beige and are omnivorous (feed on plants and animals). |
|
|
| Reptiles | ||
| Classification: | ||
|
Kingdom
Animalia (animals)
Phylum Class
Reptilia (Reptiles)
|
||
|
Common Snapping Turtle Eggs
Dreamstime Click on image to enlarge it |
|
| Common Groups of Reptiles: | |
| Turtles and Tortoises: | Alligators: |
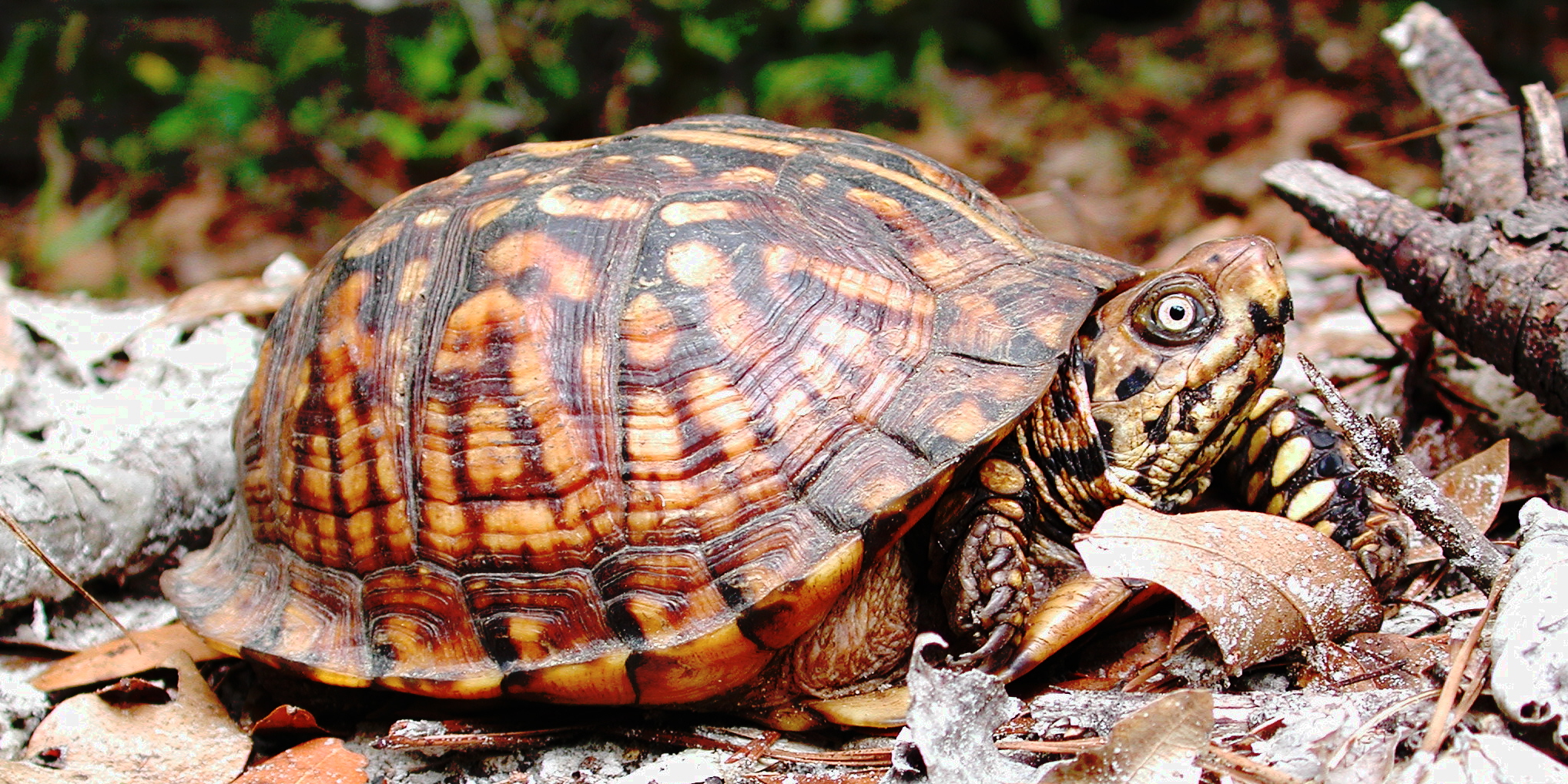
|
Eastern Box Turtle |
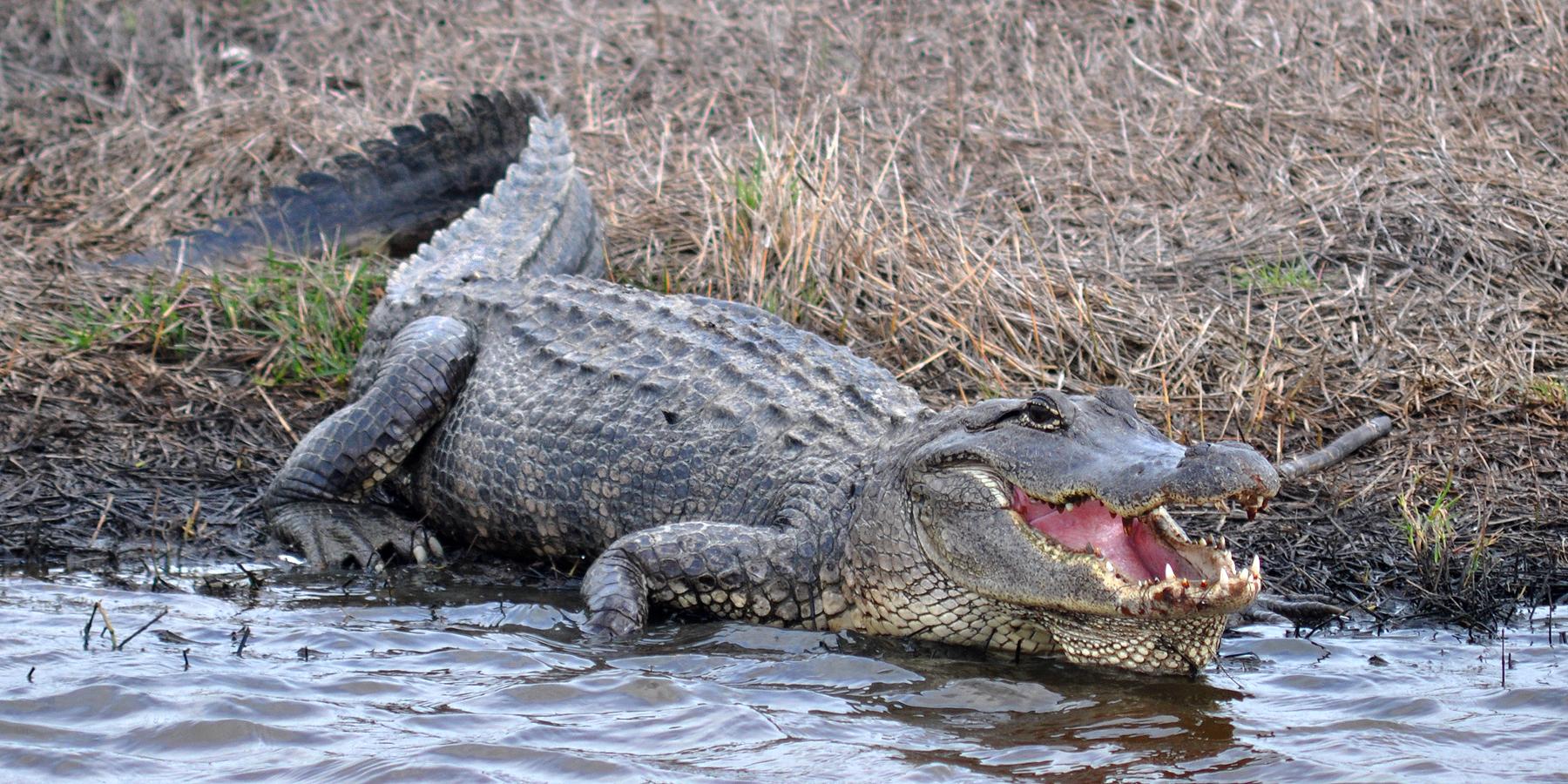
American Alligator
Wikimedia – Wilafa Click on image to enlarge it |
|
|
| Lizards: | Snakes: |
|
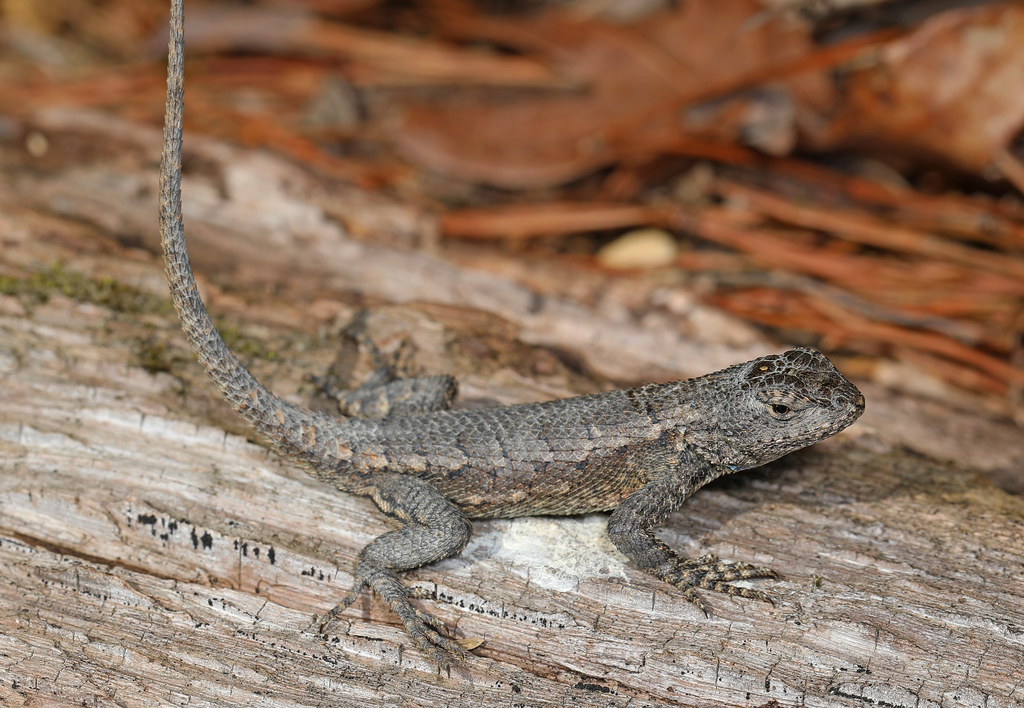
Eastern Fence Lizard |
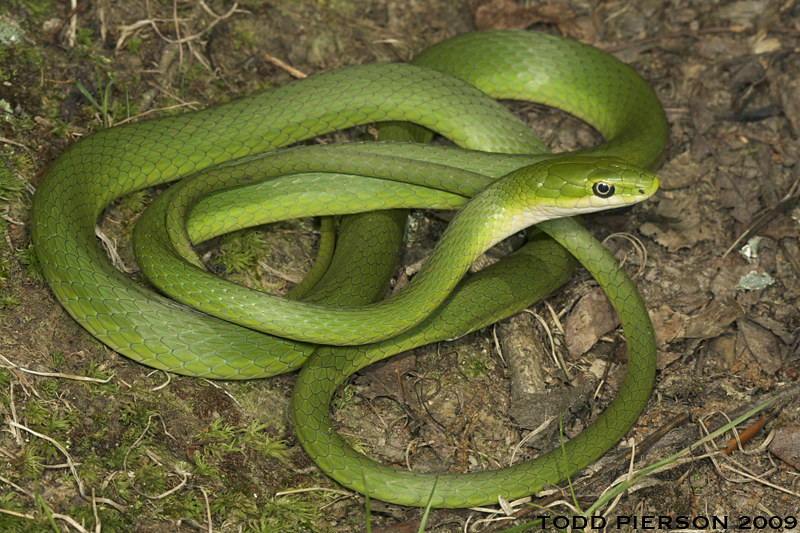
Rough Green Snake
flickr – Todd Pierson Click on image to enlarge it |
|
|
| Alabama Reptile Diversity: | ||
| #1 for turtle diversity in the United States!
31 species of turtles |
||
| Notable Reptiles of Alabama: | ||
| Alabama Red-bellied Turtle
The Alabama red-bellied turtle is the state reptile of Alabama and was once thought to be only found in Alabama. However, there are some that live in Southeastern Mississippi. They prefer sandy bottoms of shallow, slow-moving freswater streams, but they can also be found in more brackish (mixture of freshwater and salt water) waters near the bay. The Alabama red-bellied turtle is characterized by the color of the belly, which is usually light red or orange in color but can range from pale yellow to deep red. The upper shell ranges from brown to green and usually has red, orange, or yellow markings on the sides. |
Alabama Red-bellied Turtle
Wikimedia – Bill Summerour Click on image to enlarge it |
|
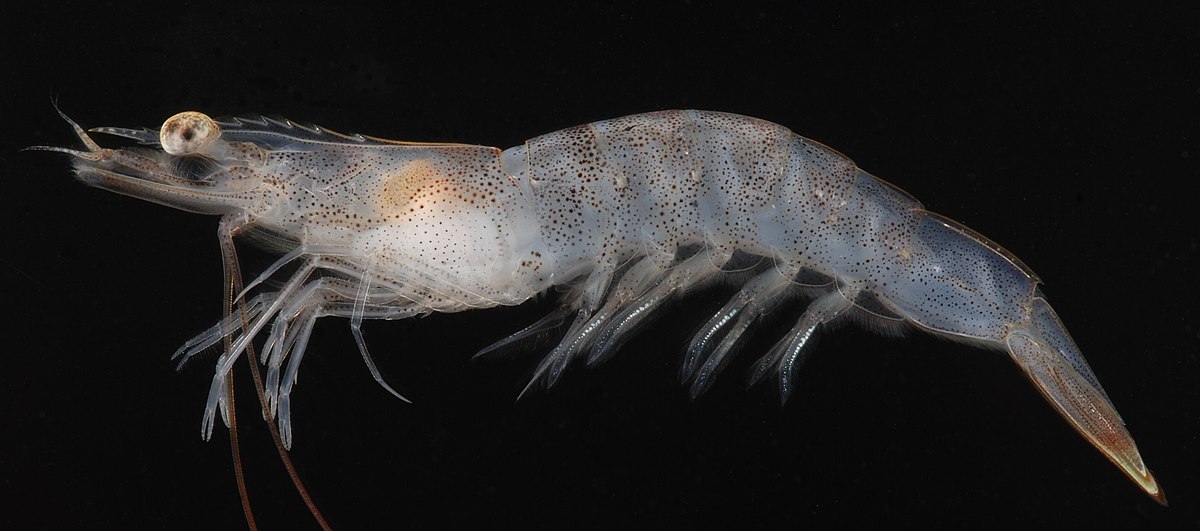
| Arthropods | |||
| They phylum Arthropoda (arthropods) is a diverse group that contains several smaller groups of recognizable organisms such as insects, crustaceans, scorpions, centipedes, and arachnids such as spiders, mites, and ticks. | |||
| Characteristics of Arthropods: | |||
|
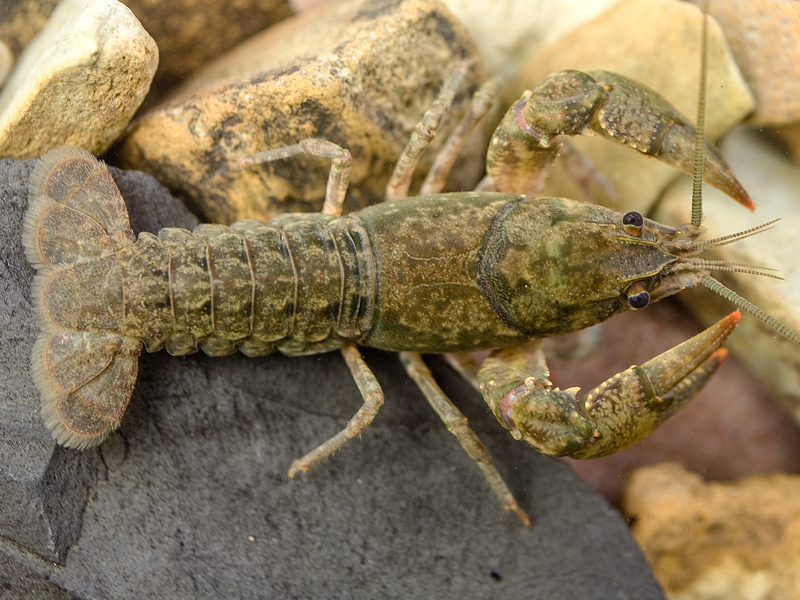
Crayfish
Dreamstime Click on image to enlarge it |
||
| Common Groups of Arthropods: | |||
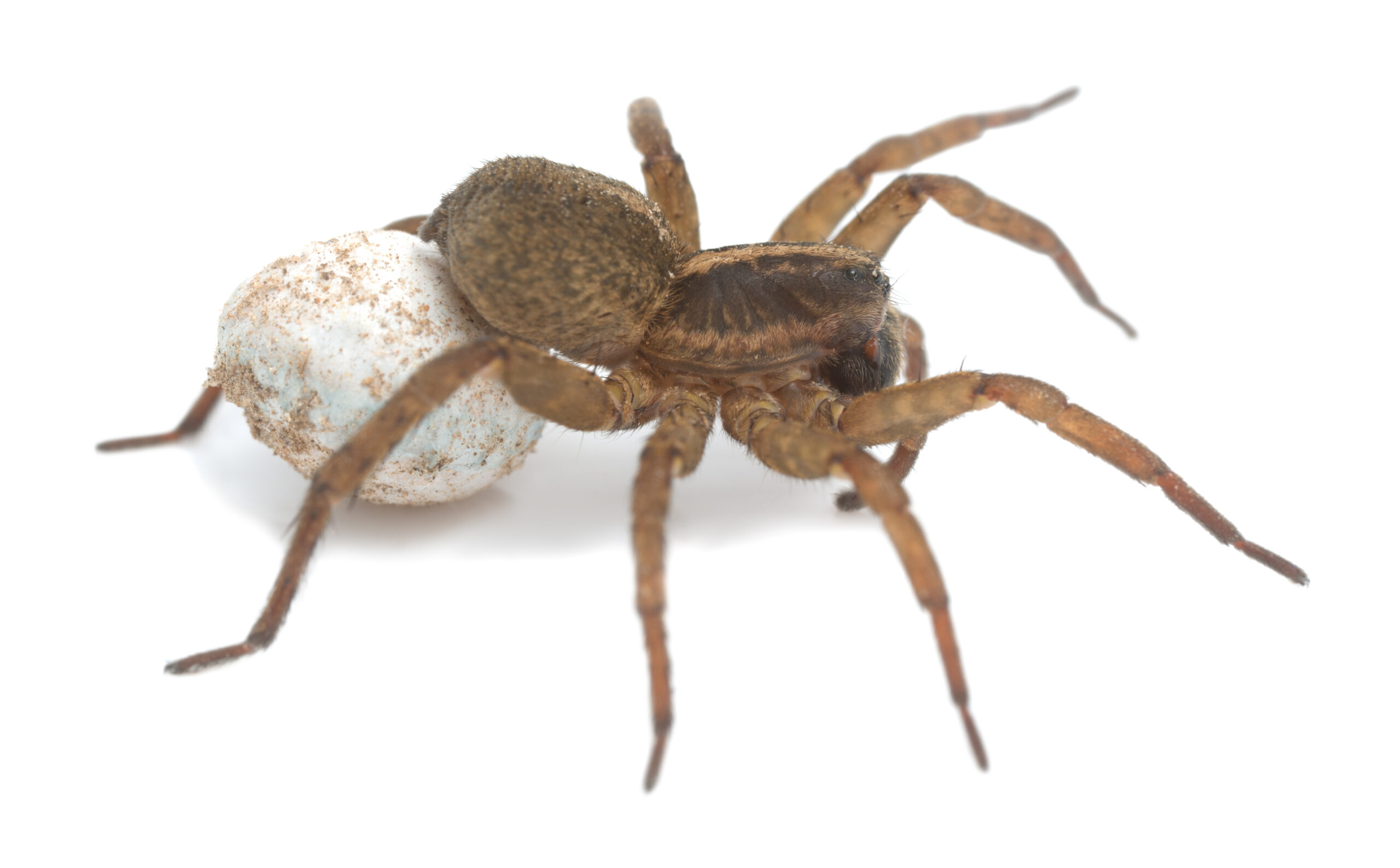
| Arachnids | |
| Classification: | Arachnid Characteristics: |
|
Kingdom
Animalia (animals)
Phylum Class |
|
| Common Groups of Arachnids: | |
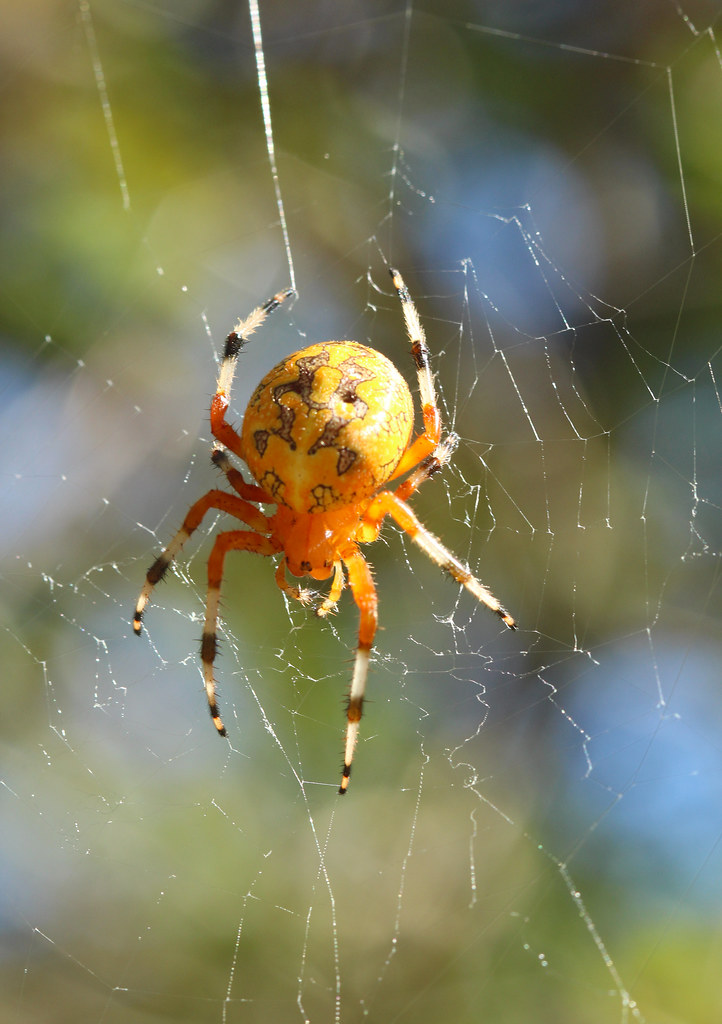
| Spiders: | Harvestmen: |
|
Marbled Orbweaver
flickr – Philip Bouchard Click on image to enlarge it |
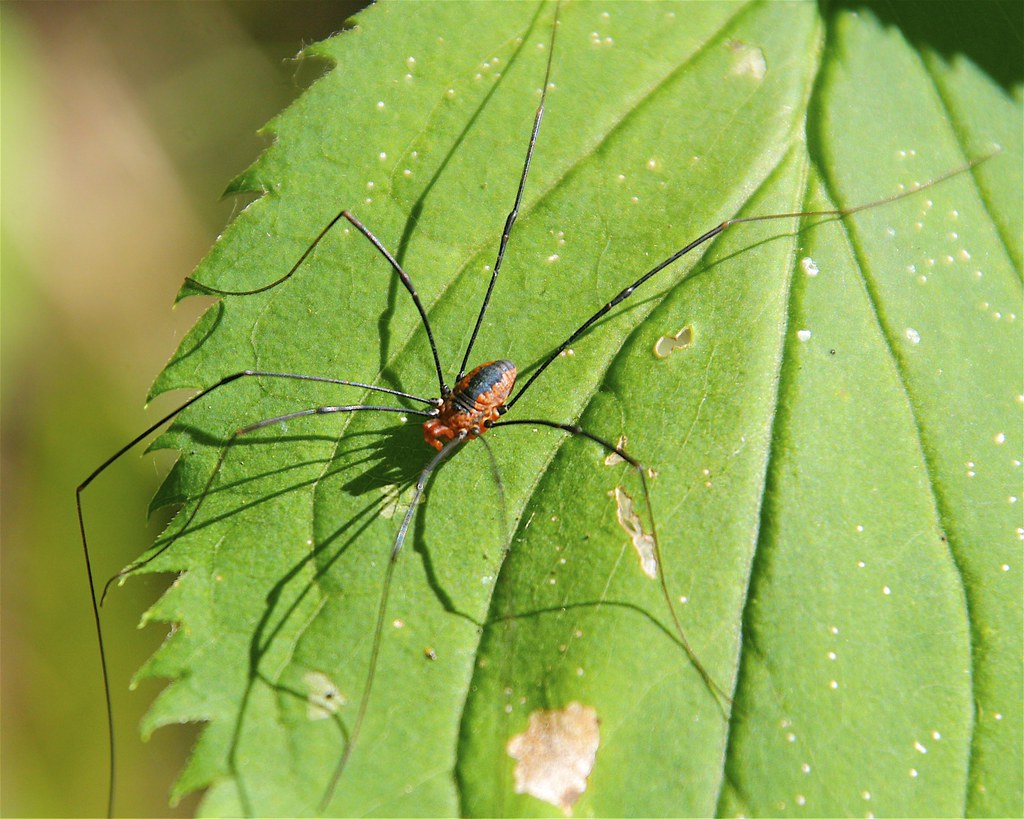
Eastern Harvestmen
flickr – Dan Mullen Click on image to enlarge it |
|
|
| Ticks and Mites: | Scorpions: |
|
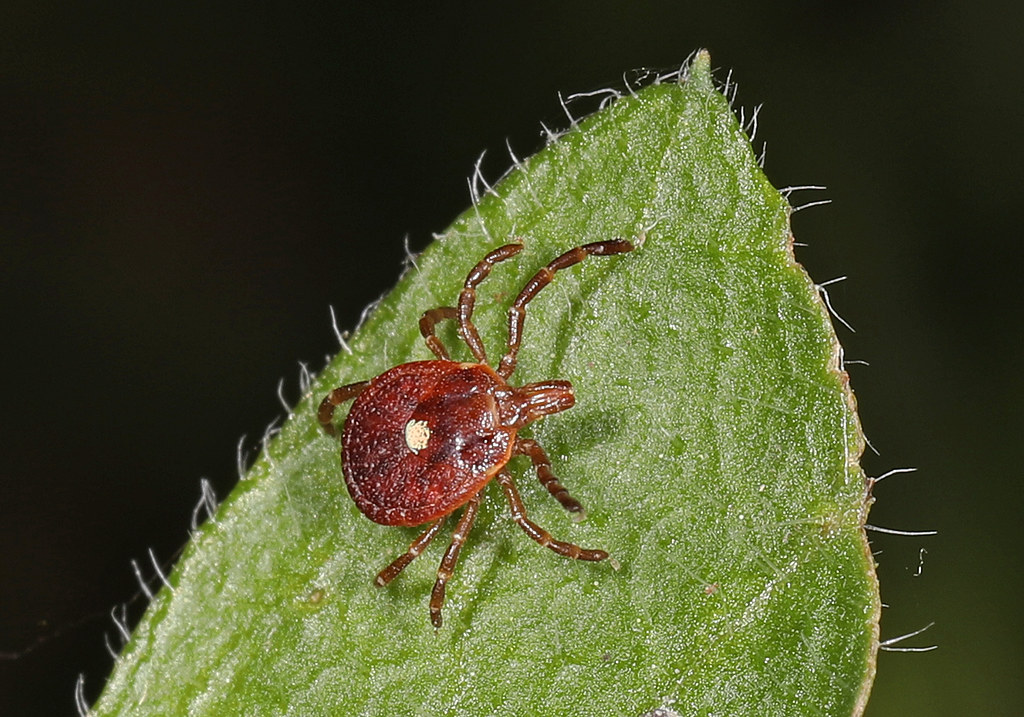
Lone Star Tick
flickr – Judy Gallagher Click on image to enlarge it |
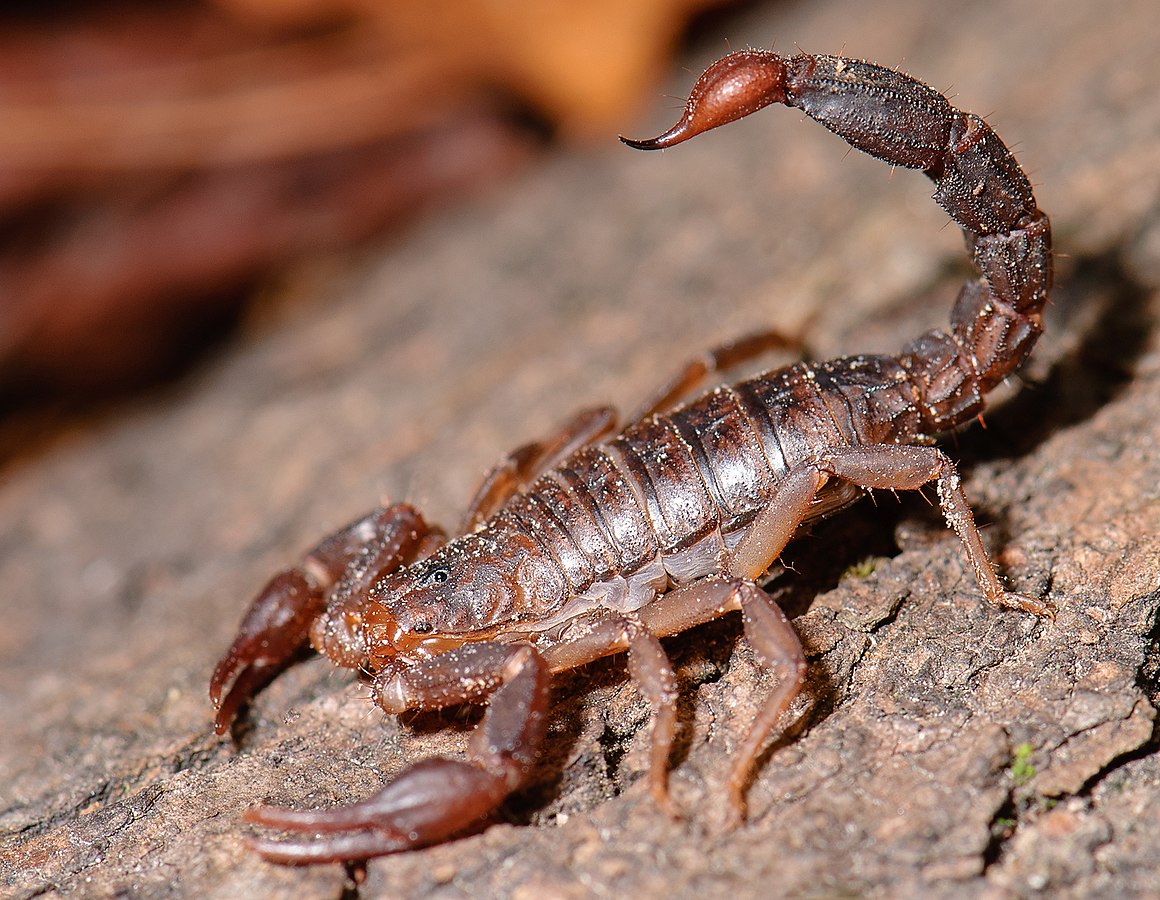
Southern Devil Scorpion
Wikimedia – Marshal Hedin Click on image to enlarge it |
|
|
| Alabama Arachnid Diversity: | |
|
92 species of spiders
4 species of ticks
2 species of scorpions
|
|
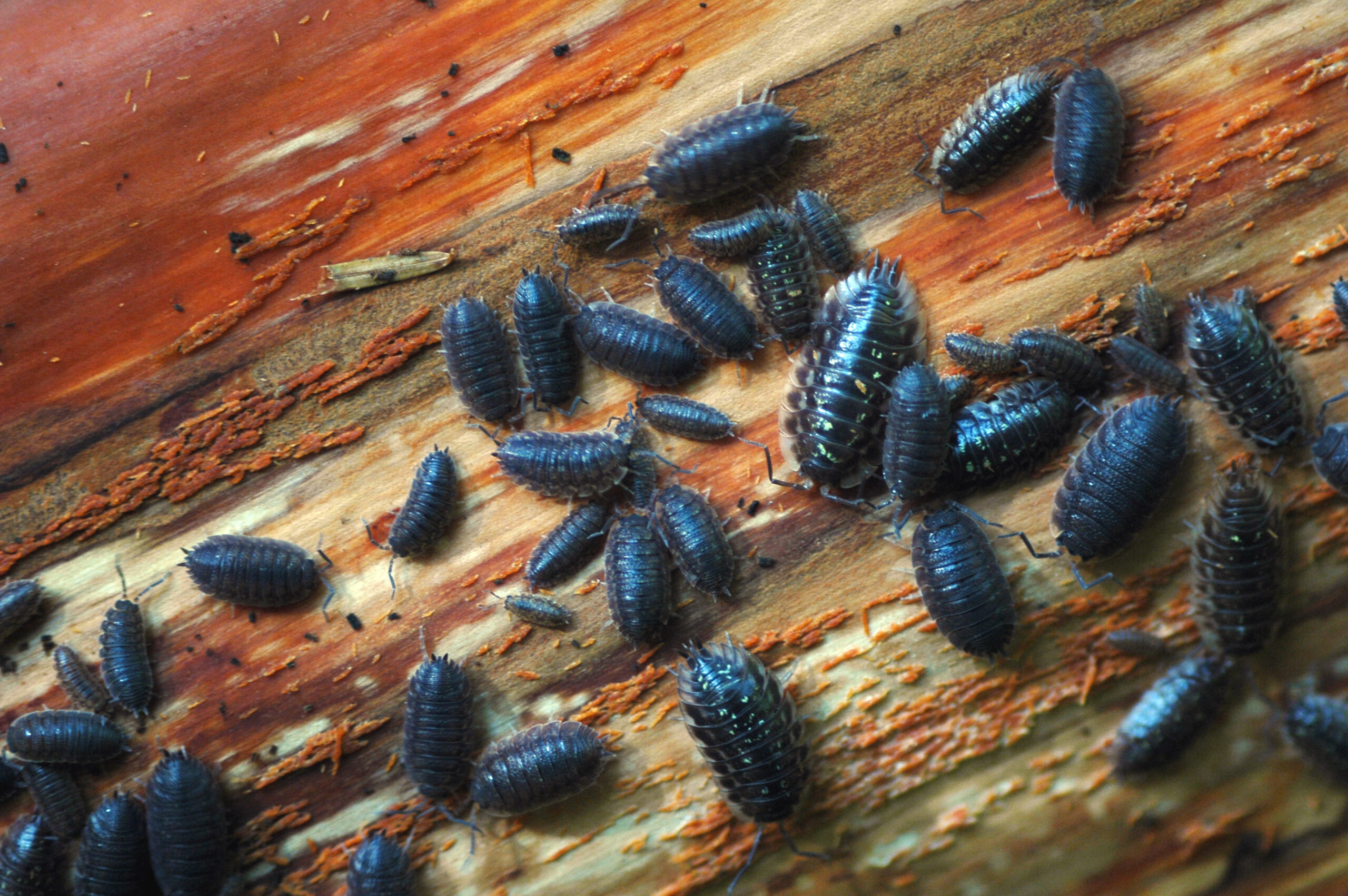
| Crustaceans | |
| Classification: | Crustacean Characteristics: |
|
Kingdom
Animalia (animals)
Phylum Subphylum |
|
| Common Groups of Crustaceans: (these 4 examples are from Class Malacostraca) |
|
| Crayfish: | Crabs: |
|
|
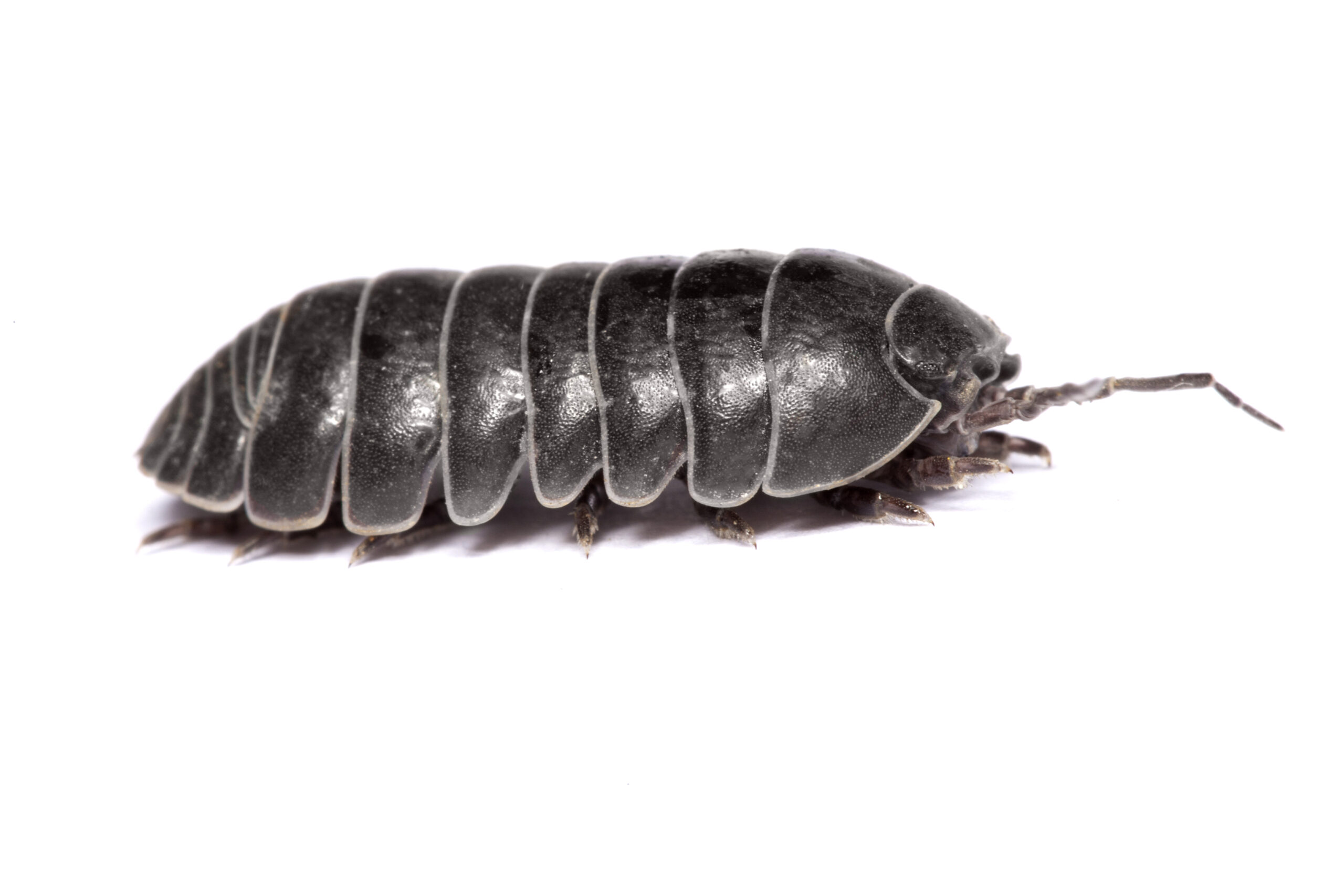
| Shrimp: | Woodlice: |
|
|
| Alabama Crustacean Diversity: | |
|
60 species of crabs
15-22 species of shrimp
97 species of crayfish
#1 in the United States for crayfish diversity! |
|
| Insects | ||
| Classification: | Insect Characteristics: | |
|
Kingdom
Animalia (animals)
Phylum
Class
Insecta (sometimes called Hexapoda): 3-part body, 3 pairs of legs |
|
|
|
Common Groups of Insects:
|
||
| There are many different types of insects that are grouped based on similar characteristics. | ||
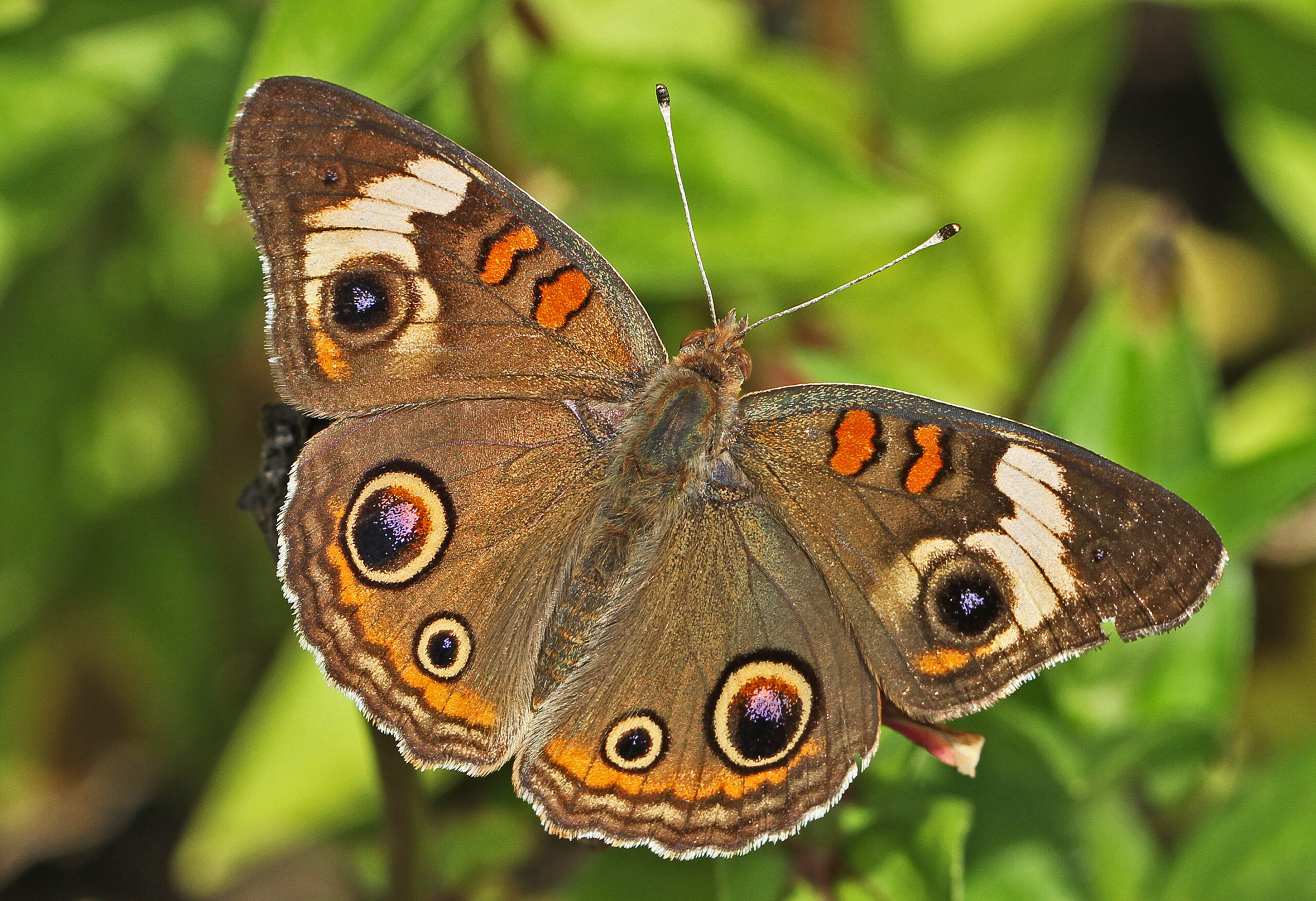
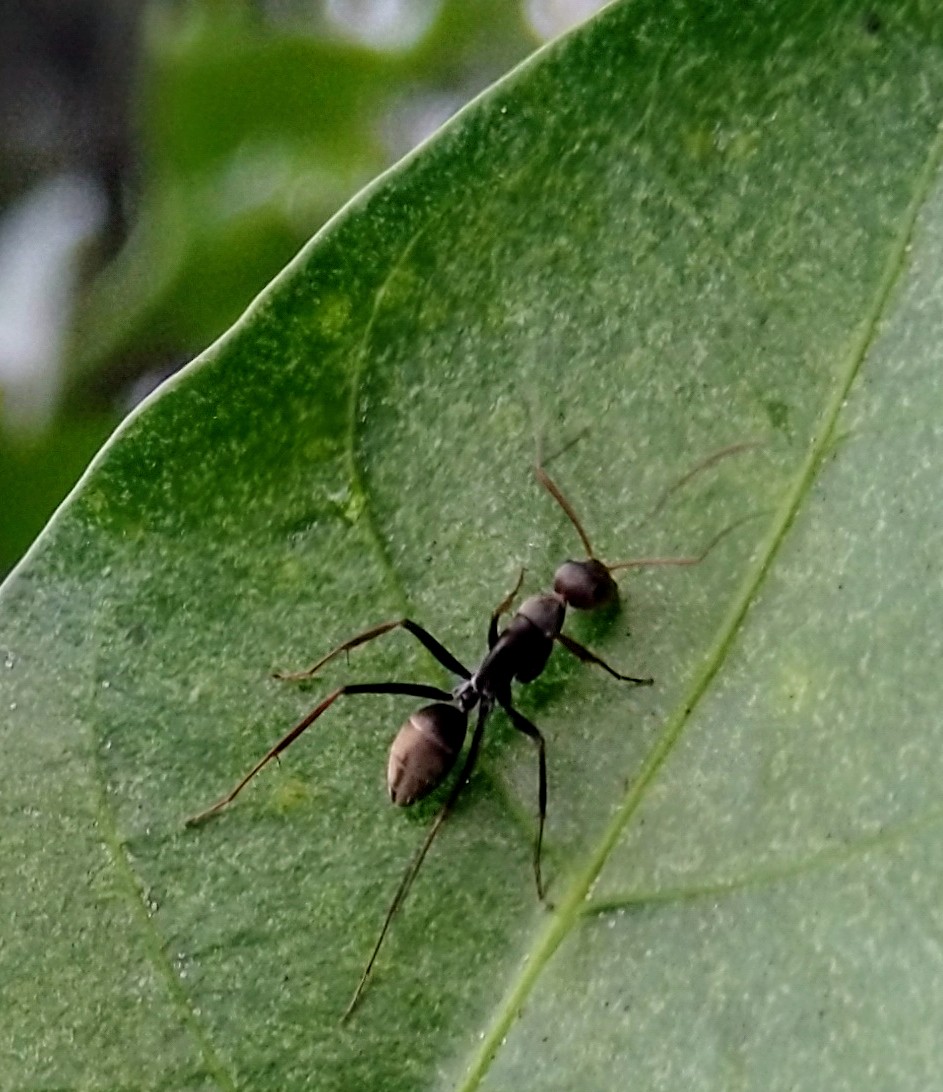
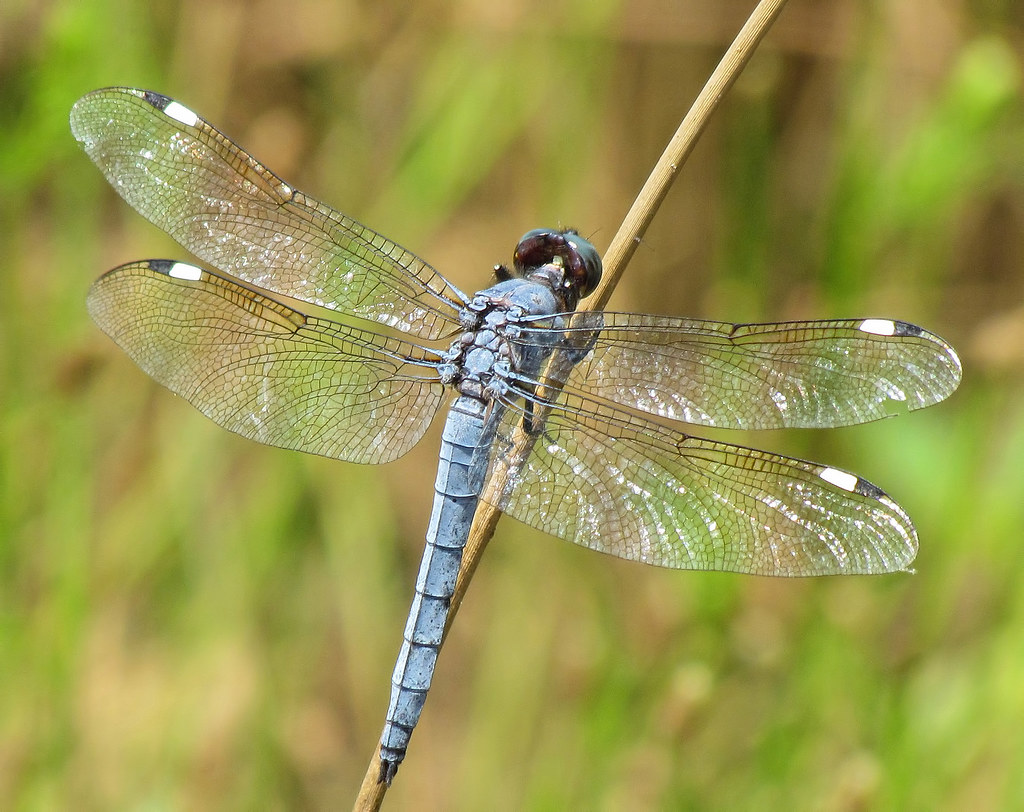
| Butterflies/Moths | Ants/Wasps/Bees | Dragonflies/Damselflies |
|
Common Buckeye
Wikimedia – Judy Gallagher Click on image to enlarge it |
Black Ant
Wikimedia – Pooja opatha Click on image to enlarge it |
Spangled Skimmer Dragonfly
flickr – Vicki DeLoach Click on image to enlarge it |
|
|
|
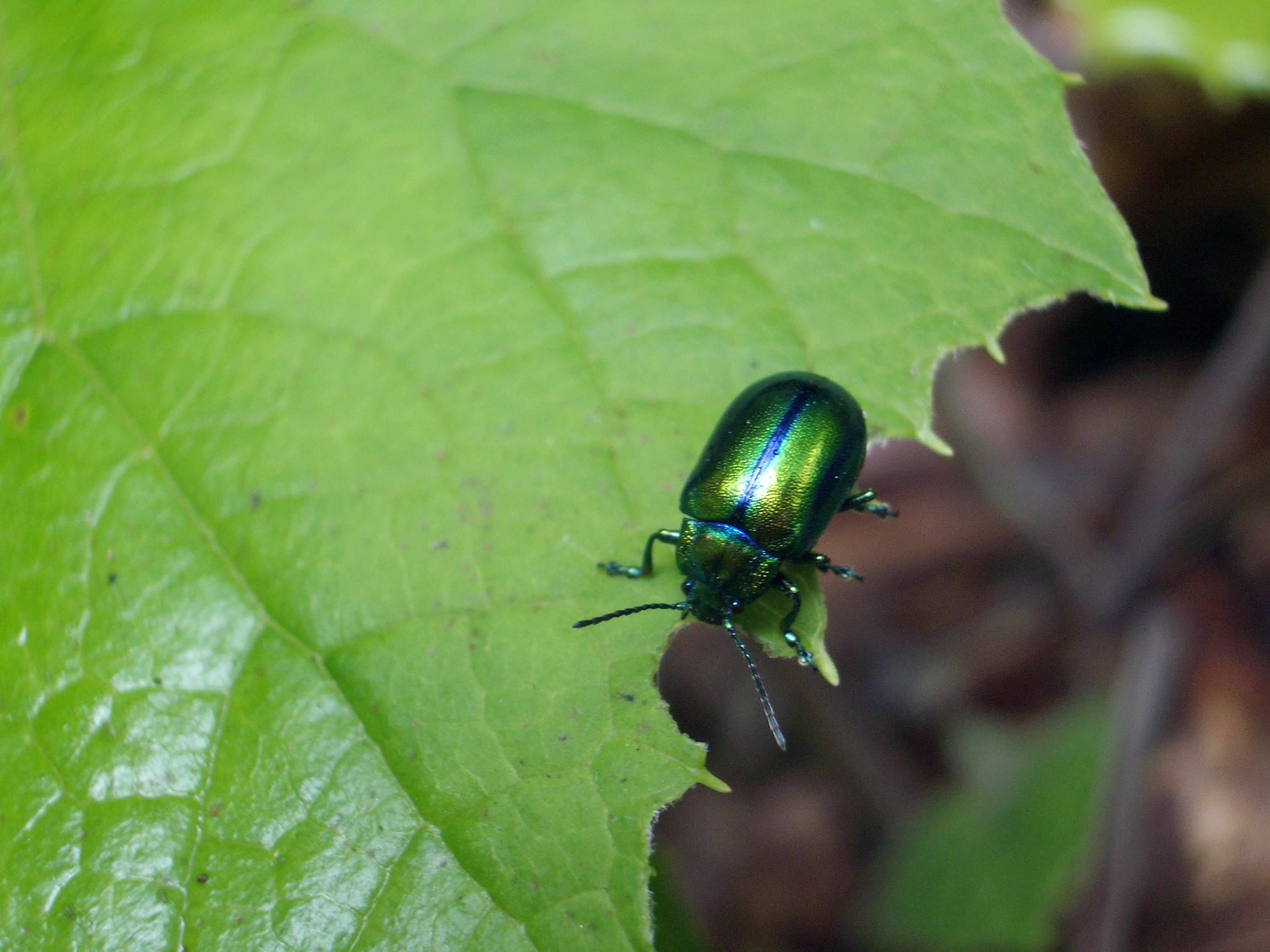
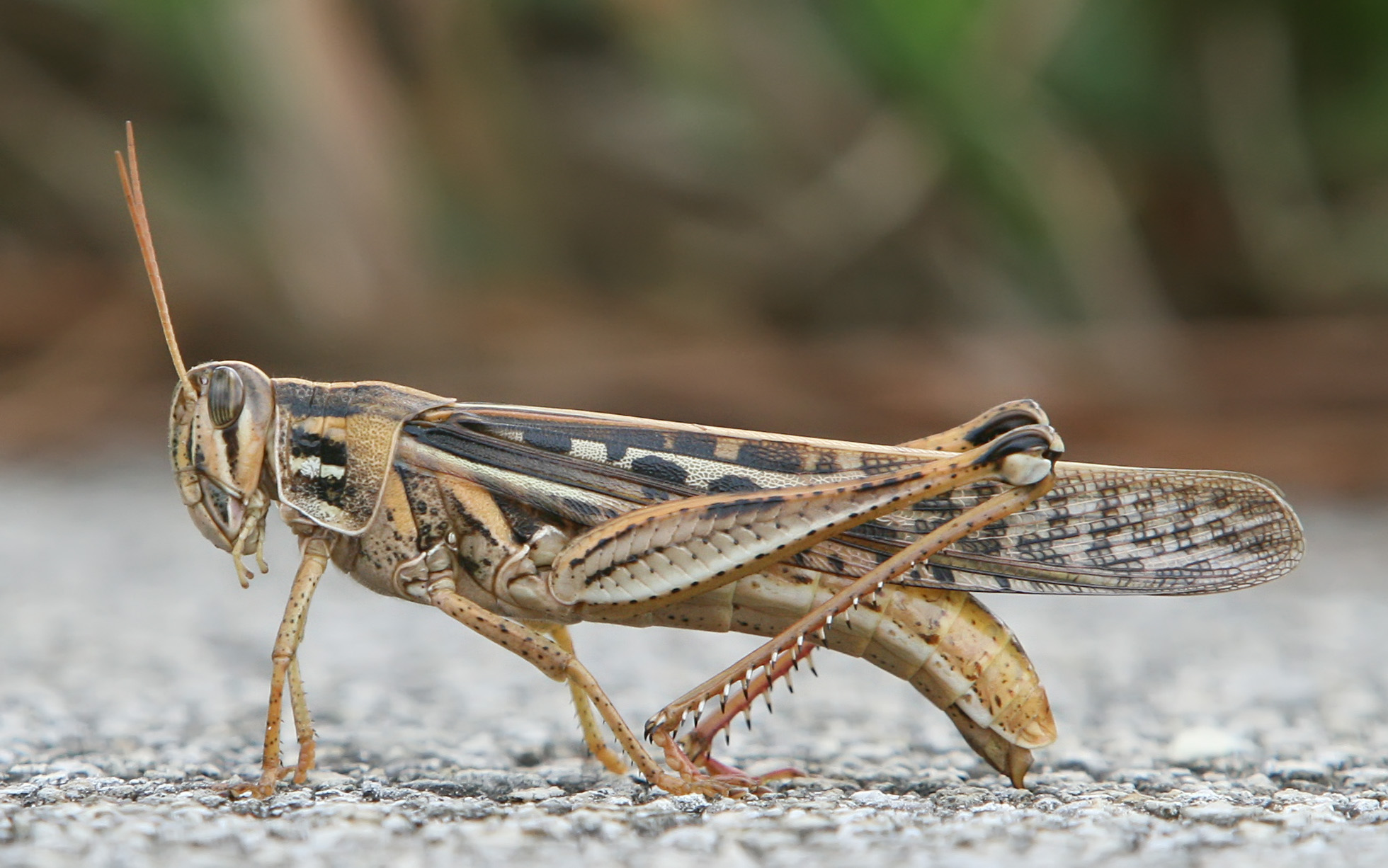
| Beetles | Flies | Grasshoppers/Crickets |
|
Leaf Beetle
Wikimedia – Cfp Click on image to enlarge it |
Fly
Wikimedia – Polychronis Rempoulakis
Click on image to enlarge it
|
American Bird Grasshopper
Wikimedia – Tomfriedel Click on imageca to enlarge it |
|
|
|
| Alabama Insect Diversity: | ||
| Not many specifics are known about the insect diversity of Alabama, but there are an estimated 20,000 arthropod (larger group that includes insects, spiders, centipedes, crustaceans, etc.) species present in the state.
157 species of butterflies |
||
| Notable Insects of Alabama: | ||
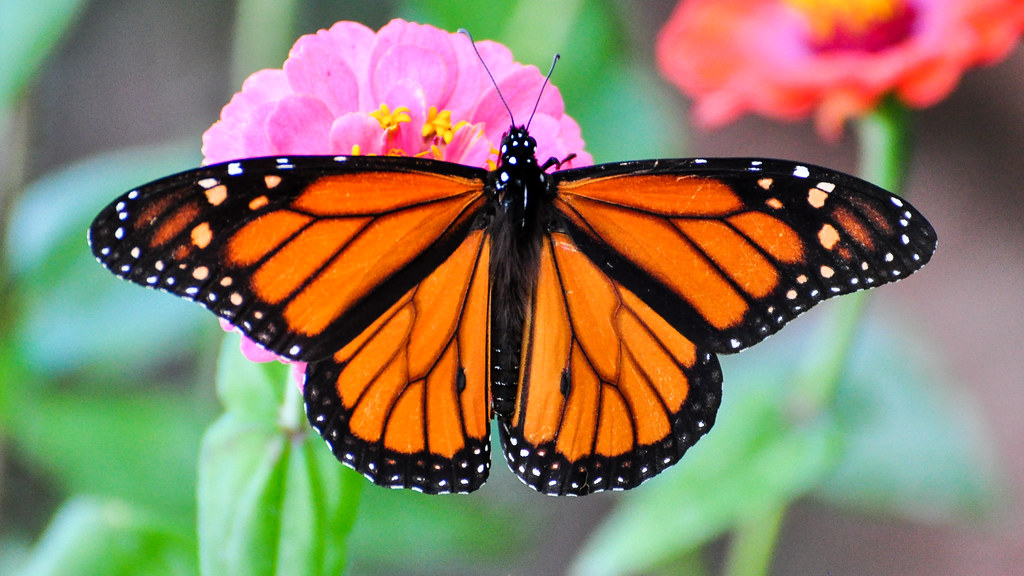
|
Monarch Butterfly
The monarch butterfly is the Alabama state insect. It is easily recognized by its bright orange wings with black borders and white spots. The monarch butterfly can be found in Alabama in the spring and summer. In the winter, they butterflies migrate to an overwintering spot in central Mexico. Monarch caterpillars feed only on milkweed, a wildflower that grows in the eastern United States. Monarch caterpillars can be identified by their bright white, yellow, and black striping. |
Monarch Butterfly
flickr – Pete Miller Click on image to enlarge it |
|
SOURCES USED FOR THIS PAGE:
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
| Biodiversity Mapping Permission Details: Text and images on the Biodiversity Mapping website are for the personal, not-for-profit use by students, scholars, educational institutions, and the public. Any such use must name "BiodiversityMapping.org" as the source for the material, with acknowledgement of BirdLife International, IUCN, NatureServe, and USGS for their contribution of the species range map data used in producing these derived works. No further permission is needed for educational use. Commercial use, electronic re-publication, or print publication of text or images is strictly prohibited without prior written permission. Jenkins, CN, KS Van Houtan, SL Pimm, JO Sexton (2015) US protected lands mismatch biodiversity priorities. PNAS 112(16), pp.5081-5086. |
||